Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Draw a plot of potential energy of a pair of nucleons as a function of their separations. Mark the regions where the nuclear force is (i) attractive and (ii) repulsive.
Draw a graph showing the variation of the potential energy of a pair of nucleons as a function of their separation. Indicate the region in which the nuclear force is (a) attractive and (b) repulsive.
Solution
The potential energy of a pair of nuclear as a function of their separation:
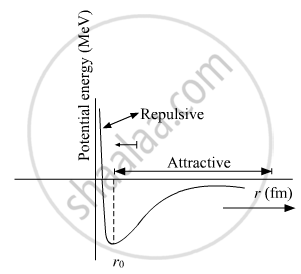
r0 is the distance at which potential energy is minimum.
For a separation greater than r0, the force is attractive and for separations less than r0 the force is strongly repulsive.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Let Fpp, Fpn and Fnn denote the magnitudes of the net force by a proton on a proton, by a proton on a neutron and by a neutron on a neutron respectively. neglect gravitational force. When the separation is 1 fm.
Two protons are kept at a separation of 10 nm. Let Fn and Fe be the nuclear force and the electromagnetic force between them.
Write two distinguishing features of nuclear forces.
Show that nuclear density is almost constant for nuclei with Z > 10.
Explain in detail the nuclear force.
Calculate the radius of the earth if the density of the earth is equal to the density of the nucleus. [mass of earth 5.97 x 1024 kg].
Relation between atomic number (Z), neutron number (N) and mass number (A) is ______.
The nuclei of isotopes of a given element differ from each other in their number of ______.
The gravitational force between a H-atom and another particle of mass m will be given by Newton’s law: `F = G(M.m)/r^2`, where r is in km and ______.
