Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2022-2023
Date & Time: 6th March 2023, 10:30 am
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
General Instructions:
Read the following instructions very carefully and strictly follow them:
- This question paper contains 35 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Question paper is divided into FIVE sections - Section A, B, C, D and E.
- Section A: Question number 1 to 18 are Multiple Choice (MCQ) type questions carrying 1 mark each:
- Section B: Question number 19 to 25 are Short Answer-1 (SA-1) type questions carrying 2 marks each.
- Section C: Question number 26 to 30 are Short Answer-2 (SA-2) type questions carrying 3 marks each
- Section D: Question number 31 to 33 are Long Answer (LA) type questions carrying 5 marks each.
- Section E: Question number 34 and 35 are Case-Based questions carrying 4 marks each.
- There is no over all choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in 2 questions in Section-B, 2 questions in Section-C, 3 questions in Section-D and 2 questions in Section E.
- Use of calculators is NOT allowed.
- c = 3 × 108 m/s
h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js
e = 1.6 × 10-19C
μ0 = 4π × 10-7T m A-1
ε0 = 8.854 × 10-12C2N-1m-2
`1/(4piε_0) = 9 xx 10^9 Nm^2C^-2`
Mass of electron = (me) = 9.1 × 10-31 kg
Mass of Neutron = 1.675 × 10-27kg
Mass of proton = 1.673 × 10-27kg
Avogadro's number = 6.023 × 1023 per gram mole
Boltzmann constant = 1.38 × 10-23 Jk-1
- c = 3 × 108 m/s
A charge Q is placed at the centre of a cube. The electric flux through one of its faces is ______.
`Q/epsi_0`
`Q/(6epsi_0)`
`Q/(8epsi_0)`
`Q/(3epsi_0)`
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Two long parallel wires kept 2 m apart carry 3A current each, in the same direction. The force per unit length on one wire due to the other is ______.
4.5 × 10-5 Nm-1, attractive
4.5 × 10-7 N/m, repulsive
9 × 10-7 N/m, attractive
9 × 10-5 N/m, attractive
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Which of the following has a permeability less than that of free space?
Copper
Aluminium
Copper chloride
Nickel
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
A square-shaped coil of side 10 cm, having 100 turns is placed perpendicular to a magnetic field which is increasing at 1 T/s. The induced emf in the coil is ______.
0.1 V
0.5 V
0.75 V
1.0 V
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
Choose the correct option related to wavelengths (λ) of different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum.
`λ_"x-rays" < λ_"micro waves" < λ_"radio waves" < λ_"visible"`
`λ_"visible" < λ_"X-rays" < λ_"radio waves" < λ_"micro waves"`
`λ_"radio waves" < λ_"micro waves" < λ_"visible" <λ_"X-rays"`
`λ_"visible" < λ_"micro waves" < λ_"radio waves" < λ_"X-rays"`
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
In Young's double-slit experiment, the screen is moved away from the plane of the slits. What will be its effect on the following?
- The angular separation of the fringes.
- Fringe-width.
Both (i) and (ii) remain constant.
(i) remains constant, but (ii) decreases.
(i) remains constant, but (ii) increases.
Both (i) and (ii) increase.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
The energy of a photon of wavelength λ is ______.
hc λ
`(hc)/lambda`
`lambda/(hc)`
`(lambdah)/c`
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
The ratio of the nuclear densities of two nuclei having mass numbers 64 and 125 is ______.
`64/125`
`4/5`
`5/4`
1
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
During the formation of a p-n junction ______.
diffusion current keeps increasing.
drift current remains constant.
both the diffusion current and drift current remain constant.
diffusion current remains almost constant but the drift current increases till both currents become equal.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
The diagram shows the four energy levels of an electron in the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom. Identify the transition in which the emitted photon will have the highest energy.
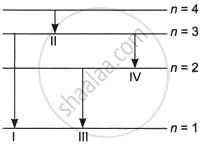
I
II
III
IV
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
The figure shows a plot of stopping potential (V0) versus `1/lambda`, where λ is the wavelength of the radiation causing photoelectric emission from a surface. The slope of the line is equal to ______.
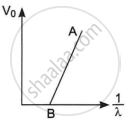
Φ0
`h/e`
`(hc)/e`
`(h^2c)/e^2`
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
The capacitors, each of 4 µF are to be connected in such a way that the effective capacitance of the combination is 6 µF. This can be achieved by connecting ______.
All three are in parallel.
All three are in series.
Two of them connected in series and the combination in parallel to the third.
Two of them connected in parallel and the combination in series to the third.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
An ideal inductor is connected across an AC source of voltage. The current in the circuit ______.
is ahead of the voltage in phase by π.
lags voltage in phase by π.
is ahead of voltage in phase by `pi"/"2`.
lags voltage in phase by `pi"/"2`.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
According to Huygens's principle, the amplitude of secondary wavelets is ______.
equal in both the forward and the backward directions.
maximum in the forward direction and zero in the backward direction.
large in the forward direction and small in the backward direction.
small in the forward direction and large in the backward direction.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
The radius of the nth orbit in the Bohr model of hydrogen is proportional to ______.
`n^2`
`1/n^2`
n
`1/n`
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
- Assertion (A): In insulators, the forbidden gap is very large.
- Reason (R): The valence electrons in an atom of an insulator are very tightly bound to the nucleus.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and (R) is NOT the correct explanation of (A).
Assertion (A) is true and Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false and Reason (R) is also false.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
- Assertion (A): The equivalent resistance between points A and B in the given networks is 2R.
- Reason (R): All the resistors are connected in parallel.
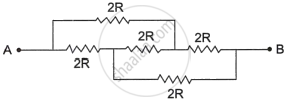
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Assertion (A) is true and Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false and Reason (R) is also false.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
- Assertion (A): The deflecting torque acting on a current-carrying loop is zero when its plane is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field.
- Reason (R): The deflecting torque acting on a loop of the magnetic moment `vecm` in a magnetic field `vecB` is given by the dot product of `vecm` and `vecB`.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Assertion (A) is true and Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false and Reason (R) is also false.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Draw a plot of potential energy of a pair of nucleons as a function of their separations. Mark the regions where the nuclear force is (i) attractive and (ii) repulsive.
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
How will the de-Broglie wavelength associated with an electron be affected when the velocity of the electron decreases? Justify your answer.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
How will the de-Broglie wavelength associated with an electron be affected when the accelerating potential is increased? Justify your answer.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Advertisements
How would the stopping potential for a given photosensitive surface change if the frequency of the incident radiation were increased? Justify your answer.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
How would the stopping potential for a given photosensitive surface change if the intensity of incident radiation was decreased? Justify your answer.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Identify the electromagnetic radiation and write its wavelength range, which is used to kill germs in water purified. Name the two sources of these radiations.
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
An electric dipole of dipole moment `vecP` is placed in a uniform electric field `vecE` with its axis inclined to the field. Write an expression for the torque `vecT` experienced by the dipole in vector form. Show diagrammatically how the dipole should be kept in the electric field so that the torque acting on it is:
- maximum
- Zero
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
Write the expression for the Lorentz force on a particle of charge q moving with a velocity `vecv` in a magnetic field `vecB`. When is the magnitude of this force maximum? Show that no work is done by this force on the particle during its motion from point `vecr_1` to point `vecr_2`.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
A long straight wire AB carries a current I. A particle (mass m and charge q) moves with a velocity `vec"v"`, parallel to the wire, at a distance d from it as shown in the figure. Obtain the expression for the force experienced by the particle and mention its directions.
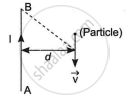
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
A potential difference (V) is applied across a conductor of length 'L' and cross-sectional area 'A'.
How will the drift velocity of electrons and the current density be affected if another identical conductor of the same material were connected in series with the first conductor? Justify your answers.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Two coils C1 and C2 are placed close to each other. The magnetic flux Φ2 linked with coil C2 varies with the current I1 flowing in coil C1 as shown in the figure. Find
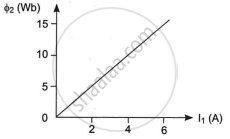
- The mutual inductance of the arrangement, and
- The rate of change of current `((dI_1)/(dt))` will induce an emf of 100V in coil C2.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
A plane wavefront propagating in a medium of refractive index 'μ1' is incident on a plane surface making the angle of incidence 'i' as shown in the figure. It enters into a medium of refractive index 'μ2' (μ2 > μ1). Use Huygens' construction of secondary wavelets to trace the propagation of the refracted wavefront. Hence verify Snell's law of refraction.
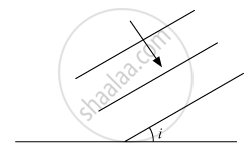
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Using Huygens's construction, show how a plane wave is reflected from a surface. Hence verify the law of reflection.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
A current of 1A flows through a coil when it is connected across a DC battery of 100V. If the DC battery is replaced by an AC source of 100 V and angular frequency of 100 rad s-1, the current reduces to 0.5 A. Find
- the impedance of the circuit.
- self-inductance of coil.
- Phase difference between the voltage and the current.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
The primary coil having NP turns of an ideal transformer is supplied with an alternating voltage VP. Obtain an expression for the voltage VS induced in its secondary coil having NS turns.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
Mention two main sources of power loss in real transformers.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
How is current sensitivity increased?
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
A galvanometer shows full-scale deflection for current Ig. A resistance R1 is required to convert it into a voltmeter of range (0 - V) and a resistance R2 to convert it into a voltmeter of range (0 - 2V). Find the resistance of the galvanometer.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Write two important limitations of Rutherford's nuclear model of the atom.
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
The wavelength of the second line of the Balmer series in the hydrogen spectrum is 4861 Å. Calculate the wavelength of the first line of the same series.
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
Advertisements
An increase in the intensity of the radiation causing photo-electric emission from a surface does not affect the maximum K.E. of the photoelectrons. Explain.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
The photon emitted during the de-excitation from the first excited level to the ground state of a hydrogen atom is used to irradiate a photocathode in which the stopping potential is 5 V. Calculate the work function of the cathode used.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Explain how free electrons in a metal at constant temperature attain an average velocity under the action of an electric field. Hence, obtain an expression for it.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Consider two conducting wires A and B of the same diameter but made of different materials joined in series across a battery. The number density of electrons in A is 1.5 times that in B. Find the ratio of the drift velocity of electrons in wire A to that in wire B.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Answer the following question.
A cell of emf E and internal resistance r is connected across a variable resistor R. Plot the shape of graphs showing a variation of terminal voltage V with (i) R and (ii) circuit current I.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Three cells, each of emf E but internal resistances 2r, 3r and 6r are connected in parallel across a resistor R.
Obtain expressions for (i) current flowing in the circuit, and (ii) the terminal potential differences across the equivalent cell.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Draw the circuit arrangement for studying V-I characteristics of a p-n junction diode in (i) forward biasing and (ii) reverse biasing. Draw the typical V-I characteristics of a silicon diode.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Describe briefly the following term:
minority carrier injection in forward biasing.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Describe briefly the following term:
breakdown voltage in reverse biasing
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Write the two processes that take place in the formation of a p-n junction.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Draw the circuit diagram of a full wave rectifier. Explain its working showing its input and output waveforms.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Write the property of a junction diode which makes it suitable for rectification of ac voltages.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Explain about the compound microscope and obtain the equation for magnification.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
In a compound microscope an object is placed at a distance of 1.5 cm from the objective of focal length 1.25 cm. If the eye-piece has a focal length of 5 cm and the final image is formed at the near point, find the magnifying power of the microscope.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Draw a ray diagram for the formation of image of an object by an astronomical telescope, in normal adjustment. Obtain the expression for its magnifying power.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
The magnifying power of an astronomical telescope in normal adjustment is 2.9 and the objective and the eyepiece are separated by a distance of 150 cm. Find the focal lengths of the two lenses.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
| A lens is a transparent optical medium bounded by two surfaces; at least one of which should be spherical. Considering image formation by a single spherical surface successively at the two surfaces of a lens, the lens maker's formula is obtained. It is useful to design lenses of desired focal length using surfaces of suitable radii of curvature. This formula helps us obtain a relation between u, v and f for a lens. Lenses form images of objects and they are used in a number of optical devices, for example, microscopes and telescopes. |
- An object AB is kept in front of a composite convex lens, as shown in the figure. Will the lens produce one image? If not, explain.

- A real image of an object formed by a convex lens is observed on a screen. If the screen is removed, will the image still be formed? Explain.
- A double convex lens is made of glass with a refractive index of 1.55 with both faces of the same radius of curvature. Find the radius of curvature required if the focal length is 20 cm.
OR
Two convex lenses A and B of focal lengths 15 cm and 10 cm respectively are placed coaxially 'd' distance apart. A point object is kept at a distance of 30 cm in front of lens A. Find the value of 'd' so that the rays emerging from lens B are parallel to its principal axis.
Chapter:
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
| A capacitor is a system of two conductors separated by an insulator. The two conductors have equal and opposite charges with a potential difference between them. The capacitance of a capacitor depends on the geometrical configuration (shape, size and separation) of the system and also on the nature of the insulator separating the two conductors. They are used to store charges. Like resistors, capacitors can be arranged in series or parallel or a combination of both to obtain the desired value of capacitance. |
- Find the equivalent capacitance between points A and B in the given diagram.

- A dielectric slab is inserted between the plates of the parallel plate capacitor. The electric field between the plates decreases. Explain.
- A capacitor A of capacitance C, having charge Q is connected across another uncharged capacitor B of capacitance 2C. Find an expression for (a) the potential difference across the combination and (b) the charge lost by capacitor A.
OR
Two slabs of dielectric constants 2K and K fill the space between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor of plate area A and plate separation d as shown in the figure. Find an expression for the capacitance of the system.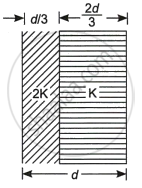
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Physics with solutions 2022 - 2023
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Physics-2023 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
