Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Choose the correct option related to wavelengths (λ) of different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Options
`λ_"x-rays" < λ_"micro waves" < λ_"radio waves" < λ_"visible"`
`λ_"visible" < λ_"X-rays" < λ_"radio waves" < λ_"micro waves"`
`λ_"radio waves" < λ_"micro waves" < λ_"visible" <λ_"X-rays"`
`λ_"visible" < λ_"micro waves" < λ_"radio waves" < λ_"X-rays"`
Solution
`λ_"radio waves" < λ_"micro waves" < λ_"visible" <λ_"X-rays"`
Explanation:
∵ E = `(hc)/lambda`
The orderly arrangement of different parts of EM wave in decreasing order of wavelength is as follows:
`λ_"radio waves" > λ_"microwaves" > λ_"IR" > λ_"visible" > λ_"UV" > λ_"X-rays" > λ_"gamma"`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The terminology of different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum is given in the text. Use the formula E = hv (for energy of a quantum of radiation: photon) and obtain the photon energy in units of eV for different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. In what way are the different scales of photon energies that you obtain related to the sources of electromagnetic radiation?
Give a reason for the following:
Long-distance radio broadcasts use short-wave bands. Why?
Moseley's Law for characteristic X-ray is √v = a(Z − b). Here,
Mark the correct options.
(a) An atom with a vacancy has smaller energy that a neutral atom.
(b) K X-ray is emitted when a hole makes a jump from the K shell to some other shell.
(c) The wavelength of K X-ray is smaller than the wavelength of L X-ray of the same material.
(d) The wavelength of Kα X-ray is smaller than the wavelength of Kβ X-ray of the same material.
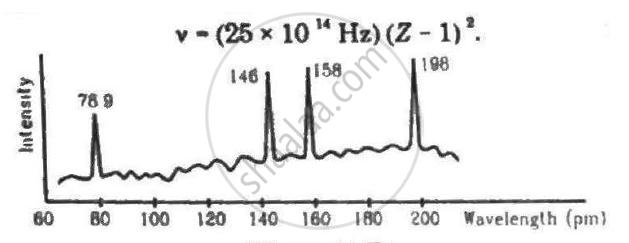
Continuous X-rays are made to strike a tissue paper soaked with polluted water. The incoming X-rays excite the atoms of the sample by knocking out the electrons from the inner shells. Characteristic X-rays are analysed and the intensity is plotted against the wavelength. Assuming that only Kα intensities are detected, list the elements present in the sample from the plot. Use Moseley's equation v − (25 × 1014Hz)(Z − 1)2.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
-
- Calculate the speed of the wave.
- Name the medium through which it is traveling.
Choose the correct option.
How does the frequency of a beam of ultraviolet light change when it travels from air into glass?
Calculate the wavelength of a microwave of a frequency of 8.0 GHz.
The area to be covered for T.V telecast is doubled then the height of transmitting antenna (T.V tower) will have to be:-
Find the photon energy in units of ev for electromagnetic wave if waves length 40 m. Given h = 6.63 × 10–34 J.
