Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Choose the correct option.
How does the frequency of a beam of ultraviolet light change when it travels from air into glass?
Options
depends on the values of μ and ε
increases
decreases
remains same
Solution
remains same
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum which is suitable for radar system used in aircraft navigation.
If the earth did not have atmosphere, would its average surface temperature be higher or lower than what it is now? Explain.
What physical quantity is the same for X-rays of wavelength 10−10 m, red light of wavelength 6800 Å and radiowaves of wavelength 500 m?
Give a reason for the following:
It is necessary to use satellites for long-distance TV transmission. Why?
The small ozone layer on top of the stratosphere is crucial for human survival. Why?
The wavelengths for the light of red and blue colours are roughly 7.8 × `10^7` m and 4.8 × `10^7` m respectively.
(a) Which colour has the greater speed in vacuum?
(b) Which colour has the greater speed in glass?
Which radiation is used for satellite communication?
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves?
(a) Gamma rays.
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves?
(a) Infrared.
Give one use of microwaves.
Name the waves used for taking photographs in dark.
Two waves A and B have wavelength 0.01 Å and 9000 Å respectively.
- Name the two waves.
- Compare the speeds of these waves when they travel in vacuum.
In a Coolidge tube, electrons strike the target and stop inside it. Does the target get more and more negatively charged as time passes?
If the current in the circuit for heating the filament is increased, the cutoff wavelength
The figure shows the intensity-wavelength relations of X-rays coming from two different Coolidge tubes. The solid curve represents the relation for the tube A in which the potential difference between the target and the filament is VA and the atomic number of the target material is ZA. These quantities are VB and ZB for the other tube. Then,
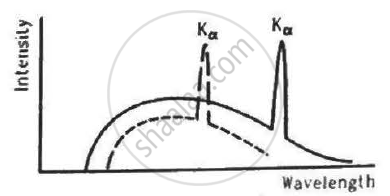
The potential difference applied to an X-ray tube is increased. As a result, in the emitted radiation,
(a) the intensity increases
(b) the minimum wavelength increases
(c) the intensity remains unchanged
(d) the minimum wavelength decreases.
X-ray incident on a material
(a) exerts a force on it
(b) transfers energy to it
(c) transfers momentum to it
(d) transfers impulse to it.
Give one use of electromagnetic radiation in Ultraviolet radiation.
Answer briefly.
Does an ordinary electric lamp emit EM waves?
Solve the numerical problem.
Calculate the wavelength in nm of an X-ray wave of frequency 2.0 × 1018 Hz.
If the Earth did not have atmosphere, would its average surface temperature be higher or lower than what it is now? Explain.
An e.m. wave exerts pressure on the surface on which it is incident. Justify.
Light of wavelength `3500A` is incident on two metals A and B whose work functions are 3.2 eV and 1.9 eV respectively. Which metal will emit photoelectrons?
Following QN ∴ 14, the radiation force on the roof will be
The frequency of e. m waves which is best suited .to observed of radius 3 × 10–4 his of the order of
Ozone layer above the earth's atmosphere will
In uranium (Z = 92) the K absorption edge is 0.107 Å and the Kα line is 0.126 Å, and the wavelength of the L absorption edge is ______.
Name the electromagnetic radiation whose frequency is 10 Hz.
Name one radiation having the wavelength longer than the wavelength of these radiations.
