Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Give a reason for the following:
It is necessary to use satellites for long-distance TV transmission. Why?
Solution
- It is necessary to use satellites for long-distance TV transmissions because television signals are of high frequencies and high energies. Thus, these signals are not reflected by the ionosphere.
- Hence, satellites are helpful in reflecting TV signals. Also, they help in long-distance TV transmissions.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How are infrared waves produced?
If the earth did not have atmosphere, would its average surface temperature be higher or lower than what it is now? Explain.
What physical quantity is the same for X-rays of wavelength 10−10 m, red light of wavelength 6800 Å and radiowaves of wavelength 500 m?
The small ozone layer on top of the stratosphere is crucial for human survival. Why?
Name the high energetic invisible electromagnetic waves which help in the study of the structure of crystals
Name the electromagnetic radiations used for (a) water purification, and (b) eye surgery.
What do you understand by the statement, "Electromagnetic waves transport momentum"?
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves?
(a) Ultraviolet
Name the region beyond the violet end of the spectrum called.
State the approximate range of wavelength associated with the ultraviolet rays.
State the approximate range of wavelength associated with visible light.
Give one use of gamma rays.
Name three properties of ultraviolet radiations which are similar to visible light.
Which part of electromagnetic spectrum is used in radar systems?
When a Coolidge tube is operated for some time it becomes hot. Where does the heat come from?
Can X-rays be polarised?
If the potential difference applied to the tube is doubled and the separation between the filament and the target is also doubled, the cutoff wavelength
One of the following wavelengths is absent and the rest are present in the X-rays coming from a Coolidge tube. Which one is the absent wavelength?
X-ray from a Coolidge tube is incident on a thin aluminium foil. The intensity of the X-ray transmitted by the foil is found to be I0. The heating current is increased to increase the temperature of the filament. The intensity of the X-ray transmitted by the foil will be
(a) zero
(b) < I0
(c) I0
(d) > I0
Cutoff wavelength of X-rays coming from a Coolidge tube depends on the
(a) target material
(b) accelerating voltage
(c) separation between the target and the filament
(d) temperature of the filament.
The electric current in an X-ray tube (from the target to the filament) operating at 40 kV is 10 mA. Assume that on an average, 1% of the total kinetic energy of the electron hitting hte target are converted into X-rays.
(a) What is the total power emitted as X-rays and (b) how much heat is produced in the target every second?
The wavelength of Kα X-ray of tungsten is 21.3 pm. It takes 11.3 keV to knock out an electron from the L shell of a tungsten atom. What should be the minimum accelerating voltage across an X-ray tube having tungsten target which allows production of Kα X-ray?
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
The Kα X-rays of aluminium (Z = 13) and zinc (Z = 30) have wavelengths 887 pm and 146 pm respectively. Use Moseley's law √v = a(Z − b) to find the wavelengths of the Kα X-ray of iron (Z = 26).
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
When 40 kV is applied across an X-ray tube, X-ray is obtained with a maximum frequency of 9.7 × 1018 Hz. Calculate the value of Planck constant from these data.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Suppose a monochromatic X-ray beam of wavelength 100 pm is sent through a Young's double slit and the interference pattern is observed on a photographic plate placed 40 cm away from the slit. What should be the separation between the slits so that the successive maxima on the screen are separated by a distance of 0.1 mm?
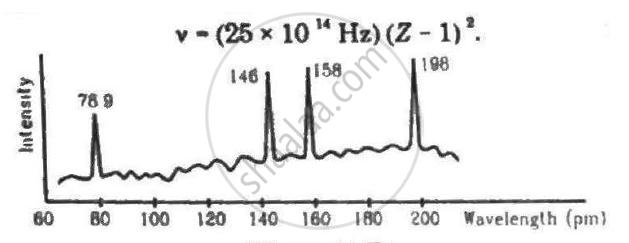
Continuous X-rays are made to strike a tissue paper soaked with polluted water. The incoming X-rays excite the atoms of the sample by knocking out the electrons from the inner shells. Characteristic X-rays are analysed and the intensity is plotted against the wavelength. Assuming that only Kα intensities are detected, list the elements present in the sample from the plot. Use Moseley's equation v − (25 × 1014Hz)(Z − 1)2.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Name the scientist who discovered Infra-red waves
Calculate the shortest wavelength of electromagnetic radiation present in Balmer series of hydrogen spectrum.
Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum used in
(i) radar and
(ii) eye surgery. Write their frequency range.
Name the radiation of the electromagnetic spectrum which is used for the following:
Radar and Give the frequency range.
Name any two electromagnetic waves which have a frequency higher than that of violet light. State one use of each.
Name two sources of infrared radiation.
State two properties of infrared radiations which differ from visible light.
State three properties of infrared radiations similar to that of visible light.
Give one use of electromagnetic radiations in Infrared radiation.
What is the wavelength of the wave whose frequency is 1012 Hz? Name the electromagnetic wave.
Choose the correct option.
Earth’s atmosphere is richest in
Choose the correct option.
How does the frequency of a beam of ultraviolet light change when it travels from air into glass?
Answer briefly.
Why are microwaves used in radar?
The area to be covered for T.V telecast is doubled then the height of transmitting antenna (T.V tower) will have to be:-
Find the photon energy in units of ev for electromagnetic wave if waves length 40 m. Given h = 6.63 × 10–34 J.
What is time period of the light for which the eye is most sensitive?
Radio waves of constant amplitude can be generated with.
SONAR emits which of the following waves?
Identify the electromagnetic wave whose wavelength range is from about 10-3 m to about 10-1 m. Write one use of this.
Name one radiation having the wavelength longer than the wavelength of these radiations.
What is the wavelength range of electromagnetic radiation used in radio broadcast?
