Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The Kα X-rays of aluminium (Z = 13) and zinc (Z = 30) have wavelengths 887 pm and 146 pm respectively. Use Moseley's law √v = a(Z − b) to find the wavelengths of the Kα X-ray of iron (Z = 26).
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Solution
Given:
Wavelength of Kα X-rays of aluminium, λ1 = 887 pm
Frequency of X-rays of aluminium is given by `nu_a = c/lambda`
`nu_a = (3 xx 10^8)/(887 xx 10^-12)`
`nu_a = 3.382 xx 10^17`
`nu_a = 33.82 xx 10^16 "Hz"`
Wavelength of Kα X-rays of zinc, `lambda_2`= 146 pm
Frequency of X-rays of zinc is given by
`nu_z = (3 xx 10^8)/(146 xx 10^-12)`
`nu_z = 0.02055 xx 10^20`
`nu_z = 2.055 xx 10^18 "Hz"`
We know
`sqrt(nu) = a(Z-b)`
For aluminium,
`5.815 xx 10^8 = a(13 - b) ...(1)`
For zinc,
`1.4331 xx 10^9 = a(30-b) ...(2)`
Dividing (1) by (2)
`(13 - b)/(30 - b) = (5.815 xx 10^-1)/1.4331`
= 0.4057
`⇒ 30 xx 0.4057 - 0.4057 b = 13 - b`
`⇒ 12.171 - 0.4057 b + b = 13`
`b = 0.829/0.5943 = 1.39491`
`a = (5.815 xx 10^8)/11.33`
`= 0.51323 xx 10^8 = 5 xx 10^7`
For Fe,
Frequency (`nu^'`) is given by
`nu^'` = 5× 107 (26 − 1.39)
= 5 × 24.61 × 107
= 123.05 × 107
`nu^' = c/lambda`
Here, c = speed of light
`lambda` = Wavelength of light
`therefore c/lambda = 5141.3 xx 10^14`
`⇒ lambda = (3 xx 10^8)/(5141.3 xx 10^14)`
`= 0.000198 xx 10^-5 "m"`
`= 198 xx 10^-12 = 198 "pm"`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name the parts of the electromagnetic spectrum which is
used to treat muscular strain.
Write in brief, how these waves can be produced.
Give a reason for the following:
It is necessary to use satellites for long-distance TV transmission. Why?
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves?
(a) Visible.
An electromagnetic wave has a frequency of 500 MHz and a wavelength of 60 cm.name the medium through which it is travelling
Consider a photon of a continuous X-ray coming from a Coolidge tube. Its energy comes from
The energy of a photon of a characteristic X-ray from a Coolidge tube comes from
For a given material, the energy and wavelength of characteristic X-rays satisfy
(a) E(Kα) > E(Kβ) > E(Kγ)
(b) E(Mα) > E(Lα) > E(Kα)
(c) λ(Kα) > λ(Kβ) > λ(Kγ)
(d) λ(Mα) > λ(Lα) > λ(Kα).
Suppose a monochromatic X-ray beam of wavelength 100 pm is sent through a Young's double slit and the interference pattern is observed on a photographic plate placed 40 cm away from the slit. What should be the separation between the slits so that the successive maxima on the screen are separated by a distance of 0.1 mm?
Arrange the following electromagnetic waves in increasing order of their frequencies (i.e. begin with the lowest frequency):
Visible light, y rays, X rays, microwaves, radio waves, infrared radiations, and ultraviolet radiation.
Name the radiation of the electromagnetic spectrum which is used for the following:
For taking photographs of the sky during the night and foggy conditions . Give the frequency range
State three properties of ultra-violet radiation similar to visible light.
Name the radiations used for the detection of fracture in bones.
X-rays, gamma rays and microwaves travelling in a vacuum have ______.
An electron beam is accelerated by a potential difference V to hit a metallic target to produce X-rays. It produces continuous as well as characteristic X-rays. If λmin is the smallest possible wavelength of X-ray in the spectrum, the variation of log λmin with log V is correctly represented in:
If λv, λx and λm Am represents the wavelength of visible light, x-ray and microwaves respectively, then ______.
All components of the electromagnetic spectrum in a vacuum have the same ______
Write two uses of the following radiation.
Gamma rays
In uranium (Z = 92) the K absorption edge is 0.107 Å and the Kα line is 0.126 Å, and the wavelength of the L absorption edge is ______.
Name one radiation having the wavelength longer than the wavelength of these radiations.
In an atom X, electrons absorb the energy from an external source. This energy “excites” the electrons from a lower-energy level to a higher-energy level around the nucleus of the atom. When electrons return to the ground state, they emit photons.
The figure below is the energy level diagram of atom X with three energy levels, E1 = 0.00eV, E2 = 1.78eV and E3 = 2.95eV. The ground state is considered 0 eV for reference. The transition of electrons takes place between levels E1 and E2.
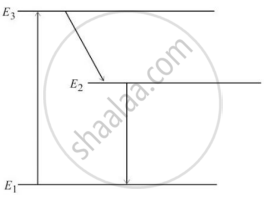
- What wavelength of radiation is needed to excite the atom to energy level E2 from E1?
- Suppose the external source has a power of 100 W. What would be the rate of photon emission?
