Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
3: Current Electricity
4: Moving Charges and Magnetism
5: Magnetism and Matter
6: Electromagnetic Induction
7: Alternating Current
▶ 8: Electromagnetic Waves
9: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
10: Wave Optics
11: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
12: Atoms
13: Nuclei
14: Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
![NCERT solutions for Physics [English] Class 12 chapter 8 - Electromagnetic Waves NCERT solutions for Physics [English] Class 12 chapter 8 - Electromagnetic Waves - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-12_6:8d092bfd54634f0fa48c49fc1b7ac4d6.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 8: Electromagnetic Waves
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 8 of CBSE NCERT for Physics [English] Class 12.
NCERT solutions for Physics [English] Class 12 8 Electromagnetic Waves Exercise [Pages 285 - 287]
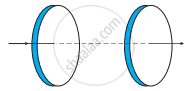
Figure shows a capacitor made of two circular plates each of radius 12 cm, and separated by 5.0 cm. The capacitor is being charged by an external source (not shown in the figure). The charging current is constant and equal to 0.15 A.
- Calculate the capacitance and the rate of charge of the potential difference between the plates.
- Obtain the displacement current across the plates.
- Is Kirchhoff’s first rule (junction rule) valid at each plate of the capacitor? Explain.
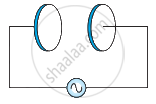
A parallel plate capacitor (Figure) made of circular plates each of radius R = 6.0 cm has a capacitance C = 100 pF. The capacitor is connected to a 230 V ac supply with a (angular) frequency of 300 rad s−1.
- What is the rms value of the conduction current?
- Is the conduction current equal to the displacement current?
- Determine the amplitude of B at a point 3.0 cm from the axis between the plates.
What physical quantity is the same for X-rays of wavelength 10−10 m, red light of wavelength 6800 Å and radiowaves of wavelength 500 m?
A plane electromagnetic wave travels in vacuum along z-direction. What can you say about the directions of its electric and magnetic field vectors? If the frequency of the wave is 30 MHz, what is its wavelength?
A radio can tune in to any station in the 7.5 MHz to 12 MHz band. What is the corresponding wavelength band?
A charged particle oscillates about its mean equilibrium position with a frequency of 109 Hz. What is the frequency of the electromagnetic waves produced by the oscillator?
The amplitude of the magnetic field part of a harmonic electromagnetic wave in vacuum is B0 = 510 nT. What is the amplitude of the electric field part of the wave?
Suppose that the electric field amplitude of an electromagnetic wave is E0 = 120 N/C and that its frequency is v = 50.0 MHz.
- Determine B0, ω, k, and λ.
- Find expressions for E and B.
The terminology of different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum is given in the text. Use the formula E = hv (for energy of a quantum of radiation: photon) and obtain the photon energy in units of eV for different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. In what way are the different scales of photon energies that you obtain related to the sources of electromagnetic radiation?
In a plane electromagnetic wave, the electric field oscillates sinusoidally at a frequency of 2.0 × 1010 Hz and amplitude 48 V m−1.
- What is the wavelength of the wave?
- What is the amplitude of the oscillating magnetic field?
- Show that the average energy density of the E field equals the average energy density of the B field.
[c = 3 × 108 m s−1]
Additional questions
Suppose that the electric field part of an electromagnetic wave in vacuum is
`vec"E" = {(3.1"N"/"C") cos[(1.8 ("rad")/"m")"y" + (5.4 xx 10^8 ("rad")/"s")"t"]}hat"i"`
(a) What is the direction of propagation?
(b) What is the wavelength λ?
(c) What is the frequency v?
(d) What is the amplitude of the magnetic field part of the wave?
(e) Write an expression for the magnetic field part of the wave.
About 5% of the power of a 100 W light bulb is converted to visible radiation. What is the average intensity of visible radiation
(a) at a distance of 1 m from the bulb?
(b) at a distance of 10 m?
Assume that the radiation is emitted isotropically and neglect reflection.
Use the formula λm T= 0.29 cm K to obtain the characteristic temperature ranges for different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. What do the numbers that you obtain tell you?
Given below are some famous numbers associated with electromagnetic radiations in different contexts in physics. State the part of the electromagnetic spectrum to which each belongs.
(a) 21 cm (wavelength emitted by atomic hydrogen in interstellar space).
(b) 1057 MHz (frequency of radiation arising from two close energy levels in hydrogen; known as Lamb shift).
(c) 2.7 K [temperature associated with the isotropic radiation filling all space-thought to be a relic of the ‘big-bang’ origin of the universe].
(d) 5890 Å - 5896 Å [double lines of sodium]
(e) 14.4 keV [energy of a particular transition in 57Fe nucleus associated with a famous high resolution spectroscopic method (Mössbauer spectroscopy)].
Answer the following questions
Give a reason for the following:
Long-distance radio broadcasts use short-wave bands. Why?
Give a reason for the following:
It is necessary to use satellites for long-distance TV transmission. Why?
Optical and radio telescopes are built on the ground but X-ray astronomy is possible only from satellites orbiting the earth. Why?
The small ozone layer on top of the stratosphere is crucial for human survival. Why?
If the earth did not have an atmosphere, would its average surface temperature be higher or lower than what it is now?
Some scientists have predicted that a global nuclear war on the earth would be followed by a severe ‘nuclear winter’ with a devastating effect on life on earth. What might be the basis of this prediction?
Solutions for 8: Electromagnetic Waves
![NCERT solutions for Physics [English] Class 12 chapter 8 - Electromagnetic Waves NCERT solutions for Physics [English] Class 12 chapter 8 - Electromagnetic Waves - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-12_6:8d092bfd54634f0fa48c49fc1b7ac4d6.jpg)
NCERT solutions for Physics [English] Class 12 chapter 8 - Electromagnetic Waves
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Physics [English] Class 12 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT solutions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 12 CBSE 8 (Electromagnetic Waves) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics [English] Class 12 chapter 8 Electromagnetic Waves are Elementary Facts About Electromagnetic Wave Uses, Electromagnetic Spectrum, Transverse Nature of Electromagnetic Waves, Electromagnetic Waves, Displacement Current.
Using NCERT Physics [English] Class 12 solutions Electromagnetic Waves exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Physics [English] Class 12 students prefer NCERT Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 8, Electromagnetic Waves Physics [English] Class 12 additional questions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 12 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
