Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Give a reason for the following:
It is necessary to use satellites for long-distance TV transmission. Why?
उत्तर
- It is necessary to use satellites for long-distance TV transmissions because television signals are of high frequencies and high energies. Thus, these signals are not reflected by the ionosphere.
- Hence, satellites are helpful in reflecting TV signals. Also, they help in long-distance TV transmissions.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How are infrared waves produced?
To which part of electromagnetic spectrum does a wave of frequency 3 × 1013 Hz belong?
To which part of the electromagnetic spectrum does a wave of frequency 5 × 1019 Hz belong?
A plane electromagnetic wave travels in vacuum along z-direction. What can you say about the directions of its electric and magnetic field vectors? If the frequency of the wave is 30 MHz, what is its wavelength?
A radio can tune in to any station in the 7.5 MHz to 12 MHz band. What is the corresponding wavelength band?
The wavelengths for the light of red and blue colours are roughly 7.8 × `10^7` m and 4.8 × `10^7` m respectively.
(a) Which colour has the greater speed in vacuum?
(b) Which colour has the greater speed in glass?
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves?
(a) Gamma rays.
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves?
(a)X-rays,
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves?
(a) Ultraviolet
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves?
(a) Micro waves .
How are X-rays produced?
Can Lα X-ray of one material have shorter wavelength than Kα X-ray of another?
Why is exposure to X-rays injurious to health but not exposure to visible light, when both are electromagnetic waves?
The energy of a photon of a characteristic X-ray from a Coolidge tube comes from
The potential difference applied to an X-ray tube is increased. As a result, in the emitted radiation,
(a) the intensity increases
(b) the minimum wavelength increases
(c) the intensity remains unchanged
(d) the minimum wavelength decreases.
Iron emits Kα X-ray of energy 6.4 keV. Calculate the times taken by an iron Kα photon to cross through a distance of 3 km.
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
The Kβ X-ray of argon has a wavelength of 0.36 nm. The minimum energy needed to ionize an argon atom is 16 eV. Find the energy needed to knock out an electron from the K shell of an argon atom.
The Kβ X-rays from certain elements are given below. Draw a Moseley-type plot of √v versus Z for Kβ radiation.
| Element | Ne | P | Ca | Mn | Zn | Br |
| Energy (keV) | 0.858 | 2.14 | 4.02 | 6.51 | 9.57 | 13.3 |
Find the maximum potential difference which may be applied across an X-ray tube with tungsten target without emitting any characteristic K or L X-ray. The energy levels of the tungsten atom with an electron knocked out are as follows.
| Cell containing vacancy | K | L | M |
| Energy in keV | 69.5 | 11.3 | 2.3 |
The Kα and Kβ X-rays of molybdenum have wavelengths 0.71 A and 0.63 A respectively. Find the wavelength of Lα X-ray of molybdenum.
The energy of a silver atom with a vacancy in K shell is 25.31 keV, in L shell is 3.56 keV and in M shell is 0.530 keV higher than the energy of the atom with no vacancy. Find the frequency of Kα, Kβ and Lα X-rays of silver.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
The electron beam in a colour TV is accelerated through 32 kV and then strikes the screen. What is the wavelength of the most energetic X-ray photon?
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
When 40 kV is applied across an X-ray tube, X-ray is obtained with a maximum frequency of 9.7 × 1018 Hz. Calculate the value of Planck constant from these data.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
An X-ray tube operates at 40 kV. Suppose the electron converts 70% of its energy into a photon at each collision. Find the lowest there wavelengths emitted from the tube. Neglect the energy imparted to the atom with which the electron collides.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Name the scientist who discovered radio waves
Name the scientist who discovered Infra-red waves
Name the scientist who discovered Ultraviolet rays
Name the radiation which can be detected by thermopile.
Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum used in
(i) radar and
(ii) eye surgery. Write their frequency range.
Name the radiation of the electromagnetic spectrum which is used for the following:
Radar and Give the frequency range.
Name the radiation of the electromagnetic spectrum which is used for the following:
To photograph internal parts of the human body and Give the frequency range
Name the radiation of the electromagnetic spectrum which is used for the following:
For taking photographs of the sky during the night and foggy conditions . Give the frequency range
Name any two electromagnetic waves which have a frequency higher than that of violet light. State one use of each.
How will you investigate the existence of the radiation beyond the red and violet extremes of the spectrum?
State two properties of infrared radiations which differ from visible light.
State three properties of infrared radiations similar to that of visible light.
State three properties of ultra-violet radiation similar to visible light.
Answer briefly.
Give two uses of radio waves.
Solve the numerical problem.
The speed of light is 3 × 108 m/s. Calculate the frequency of red light of a wavelength of 6.5 × 10−7 m.
X-rays, gamma rays and microwaves travelling in a vacuum have ______.
Find the photon energy in units of ev for electromagnetic wave if waves length 40 m. Given h = 6.63 × 10–34 J.
One requires 11eV of energy to dissociate a carbon monoxide molecule into carbon and oxygen atoms. The minimum frequency of the appropriate electromagnetic radiation to achieve the dissociation lies in ______.
The electric field intensity produced by the radiations coming from 100 W bulb at a 3 m distance is E. The electric field intensity produced by the radiations coming from 50 W bulb at the same distance is ______.
Write two uses of the following radiation.
Gamma rays
The half-value thickness of an absorber is defined as the thickness that will reduce exponentially the intensity of a beam of particles by a factor of 2. The half-value thickness in (µm) for lead assuming X-ray beam of wavelength 20 pm, µ = 50 cm-1 for X-rays in lead at wavelength λ = 20 pm, is ______ µm.
Which is the correct ascending order of wavelengths?
Give any two uses of infrared waves.
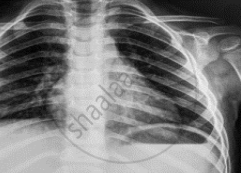
Name the electromagnetic radiation that has been used in obtaining the image below.