Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A plane electromagnetic wave travels in vacuum along z-direction. What can you say about the directions of its electric and magnetic field vectors? If the frequency of the wave is 30 MHz, what is its wavelength?
उत्तर
The electromagnetic wave travels in a vacuum along the z-direction. The electric field (E) and the magnetic field (H) are in the x-y plane and mutually perpendicular.
Frequency of the wave, v = 30 MHz = 30 × 106 s−1
Speed of light in a vacuum, c = 3 × 108 m/s
Wavelength of a wave is given as:
`lambda = "c"/"v"`
= `(3 xx 10^8)/(30 xx 10^6)`
= 10 m
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum which is suitable for radar system used in aircraft navigation.
Name the parts of the electromagnetic spectrum which is
used as a diagnostic tool in medicine.
Write in brief, how these waves can be produced.
A radio can tune in to any station in the 7.5 MHz to 12 MHz band. What is the corresponding wavelength band?
Give a reason for the following:
It is necessary to use satellites for long-distance TV transmission. Why?
An X-ray beam can be deflected
Frequencies of Kα X-rays of different materials are measured. Which one of the graphs in the figure may represent the relation between the frequency v and the atomic number Z ?

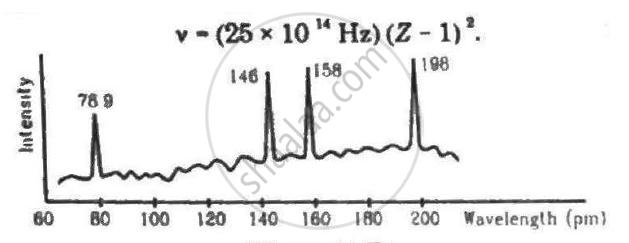
Continuous X-rays are made to strike a tissue paper soaked with polluted water. The incoming X-rays excite the atoms of the sample by knocking out the electrons from the inner shells. Characteristic X-rays are analysed and the intensity is plotted against the wavelength. Assuming that only Kα intensities are detected, list the elements present in the sample from the plot. Use Moseley's equation v − (25 × 1014Hz)(Z − 1)2.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Name three radiations and their wavelength range which are invisible and beyond the violet end of the visible spectrum.
Arrange the following electromagnetic waves in increasing order of their frequencies (i.e. begin with the lowest frequency):
Visible light, y rays, X rays, microwaves, radio waves, infrared radiations, and ultraviolet radiation.
Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum used in
(i) radar and
(ii) eye surgery. Write their frequency range.
How will you investigate the existence of the radiation beyond the red and violet extremes of the spectrum?
Name two sources of infrared radiation.
State three properties of ultra-violet radiation similar to visible light.
Radio waves of constant amplitude can be generated with.
If λv, λx and λm Am represents the wavelength of visible light, x-ray and microwaves respectively, then ______.
Electromagnetic waves with wavelength
- λ1 is used in satellite communication.
- λ2 is used to kill germs in water purifies.
- λ3 is used to detect leakage of oil in underground pipelines.
- λ4 is used to improve visibility in runways during fog and mist conditions.
- Identify and name the part of electromagnetic spectrum to which these radiations belong.
- Arrange these wavelengths in ascending order of their magnitude.
- Write one more application of each.
In an atom X, electrons absorb the energy from an external source. This energy “excites” the electrons from a lower-energy level to a higher-energy level around the nucleus of the atom. When electrons return to the ground state, they emit photons.
The figure below is the energy level diagram of atom X with three energy levels, E1 = 0.00eV, E2 = 1.78eV and E3 = 2.95eV. The ground state is considered 0 eV for reference. The transition of electrons takes place between levels E1 and E2.
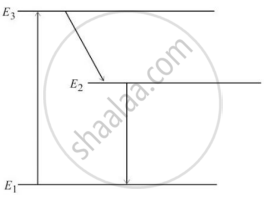
- What wavelength of radiation is needed to excite the atom to energy level E2 from E1?
- Suppose the external source has a power of 100 W. What would be the rate of photon emission?
Name two electromagnetic waves of wavelength smaller than that of violet light.
