Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What physical quantity is the same for X-rays of wavelength 10−10 m, red light of wavelength 6800 Å and radiowaves of wavelength 500 m?
उत्तर
The speed of light (3 × 108 m/s) in a vacuum is the same for all wavelengths. It is independent of the wavelength in the vacuum.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why are microwaves considered suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation?
How are infrared waves produced?
State an additional use of the X-rays waves
(a) Give a list of at least five radiations, in order of their increasing frequencies, which make up the complete electromagnetic spectrum.
(b) Which of the radiation mentioned by you in part (a) has the highest penetrating power.
What do you understand by the invisible spectrum?
Name three properties of ultraviolet radiations which are similar to visible light.
How are X-rays produced?
Characteristic X-rays may be used to identify the element from which they are being emitted. Can continuous X-rays be used for this purpose?
One of the following wavelengths is absent and the rest are present in the X-rays coming from a Coolidge tube. Which one is the absent wavelength?
For harder X-rays,
(a) the wavelength is higher
(b) the intensity is higher
(c) the frequency is higher
(d) the photon energy is higher.
The energy of a silver atom with a vacancy in K shell is 25.31 keV, in L shell is 3.56 keV and in M shell is 0.530 keV higher than the energy of the atom with no vacancy. Find the frequency of Kα, Kβ and Lα X-rays of silver.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Name the scientist who discovered Visible light
Name the scientist who discovered Ultraviolet rays
Name the part of the electromagnetic spectrum which is:
Suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation.
Name two sources of infrared radiation.
State three properties of infrared radiations similar to that of visible light.
Name the e.m. waves which are suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation. Write the range of frequency of these waves.
The ratio of contributions made by the electric field and magnetic field components to the intensity of an EM wave is ______.
Which is the correct ascending order of wavelengths?
In an atom X, electrons absorb the energy from an external source. This energy “excites” the electrons from a lower-energy level to a higher-energy level around the nucleus of the atom. When electrons return to the ground state, they emit photons.
The figure below is the energy level diagram of atom X with three energy levels, E1 = 0.00eV, E2 = 1.78eV and E3 = 2.95eV. The ground state is considered 0 eV for reference. The transition of electrons takes place between levels E1 and E2.
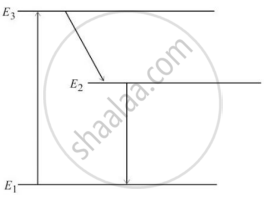
- What wavelength of radiation is needed to excite the atom to energy level E2 from E1?
- Suppose the external source has a power of 100 W. What would be the rate of photon emission?
