Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum used in
(i) radar and
(ii) eye surgery. Write their frequency range.
उत्तर
The microwave range of the electromagnetic spectrum with frequency range 1.6 to 300 GHz and wavelength range 187 to 10 mm are used in operating radar and ultraviolet range with frequency 8 x 1014 Hz to 3 x 1016 Hz and wavelength 400 nm to 10 nm are used in eye surgery.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the parts of the electromagnetic spectrum which is
used to treat muscular strain.
Write in brief, how these waves can be produced.
Which radiation is used for satellite communication?
When a Coolidge tube is operated for some time it becomes hot. Where does the heat come from?
The potential difference applied to an X-ray tube is increased. As a result, in the emitted radiation,
(a) the intensity increases
(b) the minimum wavelength increases
(c) the intensity remains unchanged
(d) the minimum wavelength decreases.
The wavelength of Kα X-ray of tungsten is 21.3 pm. It takes 11.3 keV to knock out an electron from the L shell of a tungsten atom. What should be the minimum accelerating voltage across an X-ray tube having tungsten target which allows production of Kα X-ray?
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
The Kα X-rays of aluminium (Z = 13) and zinc (Z = 30) have wavelengths 887 pm and 146 pm respectively. Use Moseley's law √v = a(Z − b) to find the wavelengths of the Kα X-ray of iron (Z = 26).
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
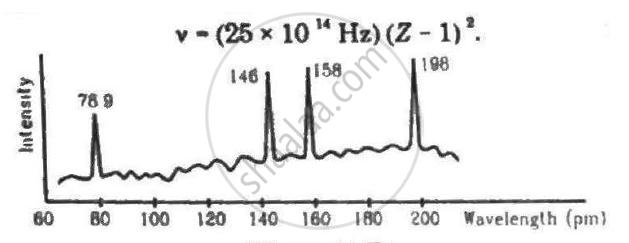
Continuous X-rays are made to strike a tissue paper soaked with polluted water. The incoming X-rays excite the atoms of the sample by knocking out the electrons from the inner shells. Characteristic X-rays are analysed and the intensity is plotted against the wavelength. Assuming that only Kα intensities are detected, list the elements present in the sample from the plot. Use Moseley's equation v − (25 × 1014Hz)(Z − 1)2.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Answer the following question.
Gamma rays and radio waves travel with the same velocity in free space. Distinguish between them in terms of their origin and the main application.
Following QN ∴ 14, the radiation force on the roof will be
What happens to the intensity of light from a bulb if the distance from the bulb is doubled? As a laser beam travels across the length of a room, its intensity essentially remains constant. What geometrical characteristic of LASER beam is responsible for the constant intensity which is missing in the case of light from the bulb?
