Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The potential difference applied to an X-ray tube is increased. As a result, in the emitted radiation,
(a) the intensity increases
(b) the minimum wavelength increases
(c) the intensity remains unchanged
(d) the minimum wavelength decreases.
उत्तर
(c) the intensity remains unchanged
(d) the minimum wavelength decreases
Cutoff wavelength (`λ_min`) is given by
`λ_min = (hc)/(eV)`
Here,
h = Planck's constant
c = Speed of light
V = Accelerating voltage
e = Charge of electron
If the potential difference applied to an X-ray tube (V) is increased, then the minimum wavelength (cutoff wavelength) gets decreased.
Intensity is not affected by the potential difference applied.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
To which part of electromagnetic spectrum does a wave of frequency 3 × 1013 Hz belong?
Why are infra-red waves often called heat waves? Explain.
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves?
(a) Visible.
State the approximate range of wavelength associated with infrared rays.
Name two electromagnetic waves of frequency smaller than that of violet light. State one use of each.
Give one use of gamma rays.
Name the rays or waves of highest frequency .
What are ultraviolet radiations?
Mark the correct options.
(a) An atom with a vacancy has smaller energy that a neutral atom.
(b) K X-ray is emitted when a hole makes a jump from the K shell to some other shell.
(c) The wavelength of K X-ray is smaller than the wavelength of L X-ray of the same material.
(d) The wavelength of Kα X-ray is smaller than the wavelength of Kβ X-ray of the same material.
X-ray incident on a material
(a) exerts a force on it
(b) transfers energy to it
(c) transfers momentum to it
(d) transfers impulse to it.
The electric current in an X-ray tube (from the target to the filament) operating at 40 kV is 10 mA. Assume that on an average, 1% of the total kinetic energy of the electron hitting hte target are converted into X-rays.
(a) What is the total power emitted as X-rays and (b) how much heat is produced in the target every second?
Name the scientist who discovered
X-rays
Name the scientist who discovered Microwaves
Name the radiation of the electromagnetic spectrum which is used for the following:
For taking photographs of the sky during the night and foggy conditions . Give the frequency range
Answer briefly.
Give two uses of radio waves.
Answer briefly.
What is a carrier wave?
Name the e.m. waves which are suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation. Write the range of frequency of these waves.
A car is moving towards a high cliff. The car driver sounds a horn of frequency f. The reflected sound heard by the driver has a frequency 2f. If v be the velocity of sound, then the velocity of the car, in the same velocity units, will be:
The area to be covered for T.V telecast is doubled then the height of transmitting antenna (T.V tower) will have to be:-
In an atom X, electrons absorb the energy from an external source. This energy “excites” the electrons from a lower-energy level to a higher-energy level around the nucleus of the atom. When electrons return to the ground state, they emit photons.
The figure below is the energy level diagram of atom X with three energy levels, E1 = 0.00eV, E2 = 1.78eV and E3 = 2.95eV. The ground state is considered 0 eV for reference. The transition of electrons takes place between levels E1 and E2.
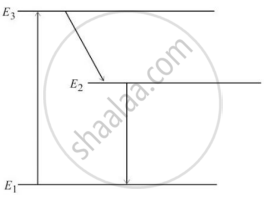
- What wavelength of radiation is needed to excite the atom to energy level E2 from E1?
- Suppose the external source has a power of 100 W. What would be the rate of photon emission?
