Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Give a reason for the following:
Long-distance radio broadcasts use short-wave bands. Why?
उत्तर
Long distance radio broadcasts use shortwave bands because only these bands can be refracted by the ionosphere.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum which is suitable for radar system used in aircraft navigation.
Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum which is:
produced by bombarding a metal target by high speed electrons.
Give a reason for the following:
It is necessary to use satellites for long-distance TV transmission. Why?
A wave has wavelength 50 Å.
- Name the wave.
- State its speed in vacuum.
- State its one use.
Name the electromagnetic radiations used for (a) water purification, and (b) eye surgery.
Arrange the following radiations in the order of their increasing wavelength:
X-rays, infrared rays, ratio waves, gamma ray and microwaves.
A wave has a wavelength of 10-3 nm. Name the wave.
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves?
(a)X-rays,
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves?
(A) Radio waves.
Name the region beyond the violet end of the spectrum called.
What do you understand by the invisible spectrum?
Give one use of gamma rays.
Two waves A and B have wavelength 0.01 Å and 9000 Å respectively.
- Name the two waves.
- Compare the speeds of these waves when they travel in vacuum.
The wavelength of X-rays is 0.01 Å. Calculate its frequency. State the assumption made, if any.
When a Coolidge tube is operated for some time it becomes hot. Where does the heat come from?
Is it possible that in a Coolidge tube characteristic Lα X-rays are emitted but not Kα X-rays?
Consider a photon of a continuous X-ray coming from a Coolidge tube. Its energy comes from
Frequencies of Kα X-rays of different materials are measured. Which one of the graphs in the figure may represent the relation between the frequency v and the atomic number Z ?

X-ray incident on a material
(a) exerts a force on it
(b) transfers energy to it
(c) transfers momentum to it
(d) transfers impulse to it.
The X-ray coming from a Coolidge tube has a cutoff wavelength of 80 pm. Find the kinetic energy of the electrons hitting the target.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
The Kβ X-rays from certain elements are given below. Draw a Moseley-type plot of √v versus Z for Kβ radiation.
| Element | Ne | P | Ca | Mn | Zn | Br |
| Energy (keV) | 0.858 | 2.14 | 4.02 | 6.51 | 9.57 | 13.3 |
The electric current in an X-ray tube (from the target to the filament) operating at 40 kV is 10 mA. Assume that on an average, 1% of the total kinetic energy of the electron hitting hte target are converted into X-rays.
(a) What is the total power emitted as X-rays and (b) how much heat is produced in the target every second?
The wavelength of Kα X-ray of tungsten is 21.3 pm. It takes 11.3 keV to knock out an electron from the L shell of a tungsten atom. What should be the minimum accelerating voltage across an X-ray tube having tungsten target which allows production of Kα X-ray?
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
The distance between the cathode (filament) and the target in an X-ray tube is 1.5 m. If the cutoff wavelength is 30 pm, find the electric field between the cathode and the target.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
The short-wavelength limit shifts by 26 pm when the operating voltage in an X-ray tube is increased to 1.5 times the original value. What was the original value of the operating voltage?
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
The electron beam in a colour TV is accelerated through 32 kV and then strikes the screen. What is the wavelength of the most energetic X-ray photon?
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Name the scientist who discovered Infra-red waves
Name the scientist who discovered Ultraviolet rays
Name three radiations and their wavelength range which are invisible and beyond the violet end of the visible spectrum.
Calculate the shortest wavelength of electromagnetic radiation present in Balmer series of hydrogen spectrum.
Define the term "Intensity" in the photon picture of electromagnetic radiation.
Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum used in
(i) radar and
(ii) eye surgery. Write their frequency range.
State three properties of ultra-violet radiation similar to visible light.
Give one use of electromagnetic radiation in Ultraviolet radiation.
Name the radiations used for the detection of fracture in bones.
Choose the correct option.
Earth’s atmosphere is richest in
Answer briefly.
Why are microwaves used in radar?
Answer briefly.
What are radio waves?
Solve the numerical problem.
The speed of light is 3 × 108 m/s. Calculate the frequency of red light of a wavelength of 6.5 × 10−7 m.
Which is the correct ascending order of wavelengths?
Name the electromagnetic radiation that has been used in obtaining the image below.
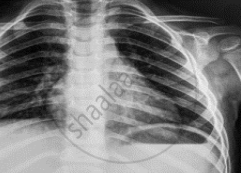
Name two electromagnetic waves of wavelength smaller than that of violet light.
