Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer briefly.
What are radio waves?
उत्तर
- Radio waves are produced by accelerated motion of charges in a conducting wire. The frequency of waves produced by the circuit depends upon the magnitudes of the inductance and the capacitance.
- Thus, by choosing suitable values of the inductance and the capacitance, radio waves of the desired frequency can be produced.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why are microwaves considered suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation?
A plane electromagnetic wave travels in vacuum along z-direction. What can you say about the directions of its electric and magnetic field vectors? If the frequency of the wave is 30 MHz, what is its wavelength?
Optical and radio telescopes are built on the ground but X-ray astronomy is possible only from satellites orbiting the earth. Why?
Why are infra-red waves often called heat waves? Explain.
What do you understand by the statement, "Electromagnetic waves transport momentum"?
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves?
(a) Micro waves .
Name two electromagnetic waves of frequency smaller than that of violet light. State one use of each.
Name two sources, each of infrared radiations and ultraviolet radiations.
In a Coolidge tube, electrons strike the target and stop inside it. Does the target get more and more negatively charged as time passes?
The energy of a photon of a characteristic X-ray from a Coolidge tube comes from
The X-ray beam emerging from an X-ray tube
The figure shows the intensity-wavelength relations of X-rays coming from two different Coolidge tubes. The solid curve represents the relation for the tube A in which the potential difference between the target and the filament is VA and the atomic number of the target material is ZA. These quantities are VB and ZB for the other tube. Then,
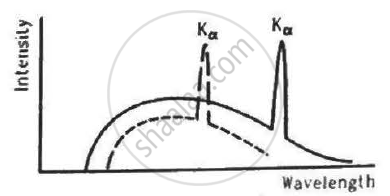
For harder X-rays,
(a) the wavelength is higher
(b) the intensity is higher
(c) the frequency is higher
(d) the photon energy is higher.
The X-ray coming from a Coolidge tube has a cutoff wavelength of 80 pm. Find the kinetic energy of the electrons hitting the target.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
The electron beam in a colour TV is accelerated through 32 kV and then strikes the screen. What is the wavelength of the most energetic X-ray photon?
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
A free atom of iron emits Kα X-rays of energy 6.4 keV. Calculate the recoil kinetic energy of the atom. Mass of an iron atom = 9.3 × 10−26 kg.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Suppose a monochromatic X-ray beam of wavelength 100 pm is sent through a Young's double slit and the interference pattern is observed on a photographic plate placed 40 cm away from the slit. What should be the separation between the slits so that the successive maxima on the screen are separated by a distance of 0.1 mm?
Name the scientist who discovered Visible light
Name the scientist who discovered Infra-red waves
Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum used in (i) radar and (ii) eye surgery. Write their frequency range.
Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum used in
(i) radar and
(ii) eye surgery. Write their frequency range.
Choose the correct option.
How does the frequency of a beam of ultraviolet light change when it travels from air into glass?
If the Earth did not have atmosphere, would its average surface temperature be higher or lower than what it is now? Explain.
A bat moving at 10 ms−1 towards a wall sends a sound signal of 8000 Hz towards it. On reflection, it hears a sound of frequency f The value of f in Hz is close to (speed of sound = 320 ms−1)
Microwaves are electromagnetic waves with frequency in the range of.
The electric field intensity produced by the radiations coming from 100 W bulb at a 3 m distance is E. The electric field intensity produced by the radiations coming from 50 W bulb at the same distance is ______.
Which is the correct ascending order of wavelengths?
Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum which:
- produces the heating effect.
- is absorbed by the ozone layer in the atmosphere.
- is used for studying crystal structure.
Write any one method of the production of each of the above radiations.
Name the electromagnetic radiation whose frequency is 10 Hz.
