Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer briefly.
Give two uses of ultraviolet rays.
उत्तर
Uses:
- Ultraviolet rays destroy germs and bacteria and hence they are used for sterilizing surgical instruments and for purification of water.
- Used in burglar alarms and security systems.
- Used to distinguish real and fake gems.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum which is:
produced by bombarding a metal target by high speed electrons.
To which part of the electromagnetic spectrum does a wave of frequency 5 × 1011 Hz belong?
A plane electromagnetic wave travels in vacuum along z-direction. What can you say about the directions of its electric and magnetic field vectors? If the frequency of the wave is 30 MHz, what is its wavelength?
The terminology of different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum is given in the text. Use the formula E = hv (for energy of a quantum of radiation: photon) and obtain the photon energy in units of eV for different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. In what way are the different scales of photon energies that you obtain related to the sources of electromagnetic radiation?
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves?
(a) Gamma rays.
Which part of electromagnetic spectrum is used in radar systems?
Characteristic X-rays may be used to identify the element from which they are being emitted. Can continuous X-rays be used for this purpose?
The figure shows the intensity-wavelength relations of X-rays coming from two different Coolidge tubes. The solid curve represents the relation for the tube A in which the potential difference between the target and the filament is VA and the atomic number of the target material is ZA. These quantities are VB and ZB for the other tube. Then,
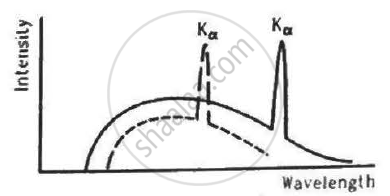
The Kβ X-ray of argon has a wavelength of 0.36 nm. The minimum energy needed to ionize an argon atom is 16 eV. Find the energy needed to knock out an electron from the K shell of an argon atom.
The Kβ X-rays from certain elements are given below. Draw a Moseley-type plot of √v versus Z for Kβ radiation.
| Element | Ne | P | Ca | Mn | Zn | Br |
| Energy (keV) | 0.858 | 2.14 | 4.02 | 6.51 | 9.57 | 13.3 |
The electric current in an X-ray tube (from the target to the filament) operating at 40 kV is 10 mA. Assume that on an average, 1% of the total kinetic energy of the electron hitting hte target are converted into X-rays.
(a) What is the total power emitted as X-rays and (b) how much heat is produced in the target every second?
The distance between the cathode (filament) and the target in an X-ray tube is 1.5 m. If the cutoff wavelength is 30 pm, find the electric field between the cathode and the target.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
An X-ray tube operates at 40 kV. Suppose the electron converts 70% of its energy into a photon at each collision. Find the lowest there wavelengths emitted from the tube. Neglect the energy imparted to the atom with which the electron collides.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
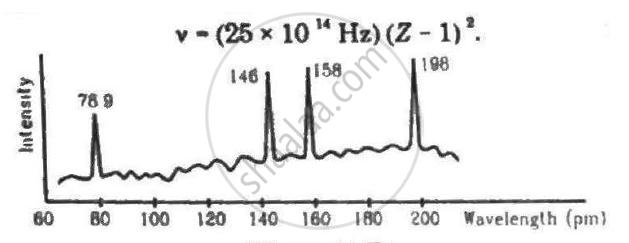
Continuous X-rays are made to strike a tissue paper soaked with polluted water. The incoming X-rays excite the atoms of the sample by knocking out the electrons from the inner shells. Characteristic X-rays are analysed and the intensity is plotted against the wavelength. Assuming that only Kα intensities are detected, list the elements present in the sample from the plot. Use Moseley's equation v − (25 × 1014Hz)(Z − 1)2.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Arrange the following electromagnetic waves in increasing order of their frequencies (i.e. begin with the lowest frequency):
Visible light, y rays, X rays, microwaves, radio waves, infrared radiations, and ultraviolet radiation.
Name the radiation of the electromagnetic spectrum which is used for the following:
To photograph internal parts of the human body and Give the frequency range
Answer the following question.
Gamma rays and radio waves travel with the same velocity in free space. Distinguish between them in terms of their origin and the main application.
Give one use of electromagnetic radiation in Ultraviolet radiation.
Answer briefly.
Can we produce a pure electric or magnetic wave in space? Why?
Answer briefly.
What is a carrier wave?
Solve the numerical problem.
Calculate the wavelength in nm of an X-ray wave of frequency 2.0 × 1018 Hz.
For television broadcasting, the frequency employed is normally
What is time period of the light for which the eye is most sensitive?
All components of the electromagnetic spectrum in a vacuum have the same ______
Identify the electromagnetic wave whose wavelength range is from about 10-12 m to about 10-8 m. Write one use of this.
Choose the correct option related to wavelengths (λ) of different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum.
What happens when an electron collides with a positron?
What is the wavelength range of electromagnetic radiation used in radio broadcast?
