Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer briefly.
Can we produce a pure electric or magnetic wave in space? Why?
उत्तर
No.
In vacuum, an electric field cannot directly induce another electric field so a “pure” electric field wave cannot exist and same can be said for a “pure” magnetic wave.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What role dose infra-red radiation play in physical therapy?
To which part of the electromagnetic spectrum does a wave of frequency 5 × 1011 Hz belong?
A radio can tune in to any station in the 7.5 MHz to 12 MHz band. What is the corresponding wavelength band?
Name the electromagnetic radiations used for (a) water purification, and (b) eye surgery.
Name the subjective property of light related to its wavelength.
Arrange the following radiations in the order of their increasing wavelength:
X-rays, infrared rays, ratio waves, gamma ray and microwaves.
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves?
(a) Visible.
Name the radiations of wavelength just longer than 8 × 10-7m.
An electromagnetic wave has a frequency of 500 MHz and a wavelength of 60 cm.name the medium through which it is travelling
The wavelength of X-rays is 0.01 Å. Calculate its frequency. State the assumption made, if any.
How are X-rays produced?
Characteristic X-rays may be used to identify the element from which they are being emitted. Can continuous X-rays be used for this purpose?
50% of the X-ray coming from a Coolidge tube is able to pass through a 0.1 mm thick aluminium foil. The potential difference between the target and the filament is increased. The thickness of the aluminium foil that will allow 50% of the X-ray to pass through will be
The wavelength of Kα X-ray of tungsten is 21.3 pm. It takes 11.3 keV to knock out an electron from the L shell of a tungsten atom. What should be the minimum accelerating voltage across an X-ray tube having tungsten target which allows production of Kα X-ray?
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
If the operating potential in an X-ray tube is increased by 1%, by what percentage does the cutoff wavelength decrease?
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
The electron beam in a colour TV is accelerated through 32 kV and then strikes the screen. What is the wavelength of the most energetic X-ray photon?
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Name the scientist who discovered Ultraviolet rays
Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum used in
(i) radar and
(ii) eye surgery. Write their frequency range.
Choose the correct option.
The EM wave emitted by the Sun and responsible for heating the Earth’s atmosphere due to greenhouse effect is
Answer briefly.
Why high-frequency carrier waves are used for the transmission of audio signals?
Microwaves are electromagnetic waves with frequency in the range of.
Following QN ∴ 14, the radiation force on the roof will be
Why does microwave oven heats up a food item containing water molecules most efficiently?
Arrange the following electromagnetic radiation in the ascending order of their frequencies:
X-rays, microwaves, gamma rays, radio waves
Write two uses of the following radiation.
Gamma rays
Below is an incomplete table showing the arrangement of electromagnetic spectrum in the increasing order of their wavelength. Complete the table:
| Gamma ray | X - ray | UV rays | Visible rays | Infrared | A | Radio waves |
- Identify the radiation A.
- Name the radiation used to detect fracture in bones.
- Name one property common to both A and Radio waves.
In an atom X, electrons absorb the energy from an external source. This energy “excites” the electrons from a lower-energy level to a higher-energy level around the nucleus of the atom. When electrons return to the ground state, they emit photons.
The figure below is the energy level diagram of atom X with three energy levels, E1 = 0.00eV, E2 = 1.78eV and E3 = 2.95eV. The ground state is considered 0 eV for reference. The transition of electrons takes place between levels E1 and E2.
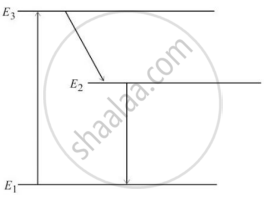
- What wavelength of radiation is needed to excite the atom to energy level E2 from E1?
- Suppose the external source has a power of 100 W. What would be the rate of photon emission?
Name two electromagnetic waves of wavelength smaller than that of violet light.
