Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Given below are some famous numbers associated with electromagnetic radiations in different contexts in physics. State the part of the electromagnetic spectrum to which each belongs.
(a) 21 cm (wavelength emitted by atomic hydrogen in interstellar space).
(b) 1057 MHz (frequency of radiation arising from two close energy levels in hydrogen; known as Lamb shift).
(c) 2.7 K [temperature associated with the isotropic radiation filling all space-thought to be a relic of the ‘big-bang’ origin of the universe].
(d) 5890 Å - 5896 Å [double lines of sodium]
(e) 14.4 keV [energy of a particular transition in 57Fe nucleus associated with a famous high resolution spectroscopic method (Mössbauer spectroscopy)].
उत्तर
(b) Radio waves; belongs to the short wavelength end.
(c) Temperature, T = 2.7°K
λm is given by Planck’s law as:
`lambda_"m" = 0.29/2.7` = 0.11 cm
This wavelength corresponds to microwaves.
(d) This is the yellow light of the visible spectrum.
(e) Transition energy is given by the relation,
E = hv
Where,
h = Planck’s constant = 6.6 × 10−34 Js
v = Frequency of radiation
Energy, E = 14.4 K eV
∴ `"v" = "E"/"h"`
= `(14.4 xx 10^3 xx 1.6 xx 10^-19)/(6.6 xx 10^-34)`
= 3.4 × 1018 Hz
This corresponds to X-rays.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
To which part of electromagnetic spectrum does a wave of frequency 3 × 1013 Hz belong?
A wave has wavelength 50 Å.
- Name the wave.
- State its speed in vacuum.
- State its one use.
A wave has a wavelength of 10-3 nm. Name the wave.
Name the region beyond the violet end of the spectrum called.
Name the radiations of wavelength just longer than 8 × 10-7m.
What potential difference should be applied across an X-ray tube to get X-ray of wavelength not less than 0.10 nm? What is the maximum energy of a photon of this X-ray in joule?
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
The X-ray coming from a Coolidge tube has a cutoff wavelength of 80 pm. Find the kinetic energy of the electrons hitting the target.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Find the maximum potential difference which may be applied across an X-ray tube with tungsten target without emitting any characteristic K or L X-ray. The energy levels of the tungsten atom with an electron knocked out are as follows.
| Cell containing vacancy | K | L | M |
| Energy in keV | 69.5 | 11.3 | 2.3 |
The Kα and Kβ X-rays of molybdenum have wavelengths 0.71 A and 0.63 A respectively. Find the wavelength of Lα X-ray of molybdenum.
If the operating potential in an X-ray tube is increased by 1%, by what percentage does the cutoff wavelength decrease?
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
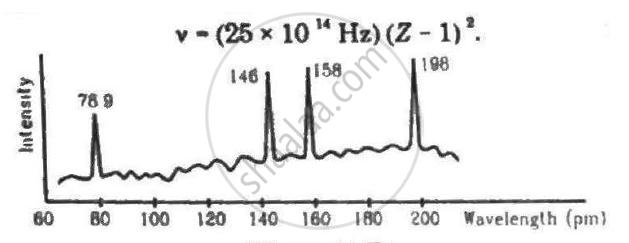
Continuous X-rays are made to strike a tissue paper soaked with polluted water. The incoming X-rays excite the atoms of the sample by knocking out the electrons from the inner shells. Characteristic X-rays are analysed and the intensity is plotted against the wavelength. Assuming that only Kα intensities are detected, list the elements present in the sample from the plot. Use Moseley's equation v − (25 × 1014Hz)(Z − 1)2.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Name the scientist who discovered radio waves
Name the part of the electromagnetic spectrum which is:
Produced by bombarding a metal target with high electrons.
Answer briefly.
What is a carrier wave?
Light of wavelength `3500A` is incident on two metals A and B whose work functions are 3.2 eV and 1.9 eV respectively. Which metal will emit photoelectrons?
Why does microwave oven heats up a food item containing water molecules most efficiently?
In uranium (Z = 92) the K absorption edge is 0.107 Å and the Kα line is 0.126 Å, and the wavelength of the L absorption edge is ______.
Identify the electromagnetic radiation and write its wavelength range, which is used to kill germs in water purified. Name the two sources of these radiations.
Name two electromagnetic waves of wavelength smaller than that of violet light.
