Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Write the expression for the Lorentz force on a particle of charge q moving with a velocity `vecv` in a magnetic field `vecB`. When is the magnitude of this force maximum? Show that no work is done by this force on the particle during its motion from point `vecr_1` to point `vecr_2`.
Solution
Lorentz force = Magnetic force + Electric force
⇒ `vecF = q(vecv xx vecB)`
`vecF = q.v.B sintheta`
when θ = 90° the Lorentz force is maximum.
If `vec(ds)` is the instantaneous displacement of charge and `vec(ds)` is also perpendicular to `vecF`.
Then,
W = `vecF. vec(ds)`
= `vecF vecs costheta`
= F.s cos90°
cos90° = 0
So, W = 0
Hence, no work is done by this force on the particle during its motion from a point `vecr_1` to point `vecr_2`.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Seema’s uncle was advised by his doctor to have an MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scan of his brain. Her uncle felt it to be expensive and wanted to postpone it. When Seema learnt about this, she took the help of her family and also approached the doctor, who also offered a substantial discount. She then convinced her uncle to undergo the test to enable the doctor to know the condition of his brain. The information thus obtained greatly helped the doctor to treat him properly.
Based on the above paragraph, answer the following questions:
(a) What according to you are the values displayed by Seema, her family and the doctor?
(b) What could be the possible reason for MRI test to be so expensive?
(c) Assuming that MRI test was performed using a magnetic field of 0.1 T, find the minimum and maximum values of the force that the magnetic field could exert on a proton (charge = 1.6 x 10-19 C) moving with a speed of 104 m/s.
According to the right-hand rule, the direction of magnetic induction if the current is directed in an anticlockwise direction is ______
A charged particle is released from rest in a region of steady and uniform electric and magnetic fields which are parallel to each other. The particle will move in a ____________.
A particle of charge -16 x 10-18 C moving with velocity 10 m/s along the X-axis enters a region where a magnetic field of induction B is along Y-axis and electric field of magnitude 104 V/m is along the negative Z-axis. If the charged particle continues moving along the X-axis, the magnitude of B is ____________.
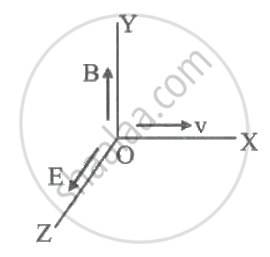
The magnetic moment is NOT associated with ____________.
Consider a wire carrying a steady current, I placed in a uniform magnetic field B perpendicular to its length. Consider the charges inside the wire. It is known that magnetic forces do no work. This implies that ______.
- motion of charges inside the conductor is unaffected by B since they do not absorb energy.
- some charges inside the wire move to the surface as a result of B.
- if the wire moves under the influence of B, no work is done by the force.
- if the wire moves under the influence of B, no work is done by the magnetic force on the ions, assumed fixed within the wire.
An electron enters with a velocity v = v0i into a cubical region (faces parallel to coordinate planes) in which there are uniform electric and magnetic fields. The orbit of the electron is found to spiral down inside the cube in plane parallel to the x-y plane. Suggest a configuration of fields E and B that can lead to it.
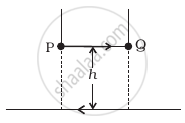
A long straight wire carrying current of 25 A rests on a table as shown in figure. Another wire PQ of length 1 m, mass 2.5 g carries the same current but in the opposite direction. The wire PQ is free to slide up and down. To what height will PQ rise?
Two long current-carrying conductors are placed parallel to each other at a distance of 8 cm between them. The magnitude of the magnetic field produced at the mid-point between the two conductors due to the current flowing in them is 300µT. The equal current flowing in the two conductors is ______.
With a neat labelled diagram, explain cyclotron motion and cyclotron formula.
