Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
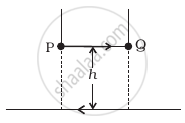
A long straight wire carrying current of 25 A rests on a table as shown in figure. Another wire PQ of length 1 m, mass 2.5 g carries the same current but in the opposite direction. The wire PQ is free to slide up and down. To what height will PQ rise?
Solution
The force is applied on PQ by a long straight wire carrying a current of 25 A which rests on a table. And the forces which other are repulsive if two straight wires are placed parallel to each other carrying current in opposite direction. Now if the wire PQ is in equilibrium then that repulsive force onPQ must balance its weight.
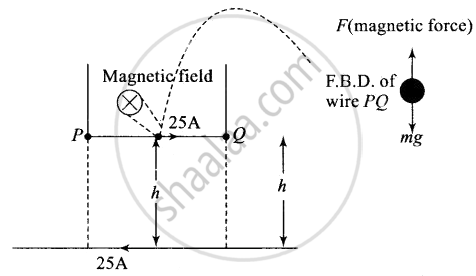
The magnetic field produced by a long straight wire carrying current of 25 A rests on a table on small wire.
`B = (mu_0I)/(2pih)`
The magnetic force on small conductor is `F = BIl sin θ = BIl`
Force applied on PQ balance the weight of small current carrying wire.
`F = mg = (mu_0I^2l)/(2pih)`
`h = (mu_0I^2l)/(2pimg) = (4pi xx 10^-7 xx (25)^2 xx 1)/(2pi xx 2.5 xx 10^-3 xx 9.8) = 51 xx 10^-4 m`
h = 0.51 cm
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A circular coil of N turns and radius R carries a current I. It is unwound and rewound to make another coil of radius R/2, current I remaining the same. Calculate the ratio of the magnetic moments of the new coil and original coil.
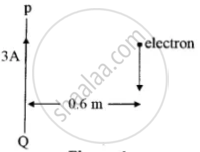
PQ is a long straight conductor carrying a current of 3A as shown in Figure below. An electron moves with a velocity of 2 x 107 ms-1 parallel to it. Find the force acting on the electron.
What is Lorentz force?
Show that currents in two long, straight, parallel wires exert forces on each other. Derive the expression for the force per unit length on each conductor.
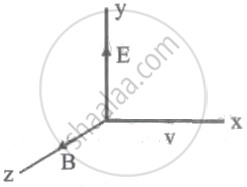
A particle with charge q moves with a velocity v in a direction perpendicular to the directions of uniform electric and magnetic fields, E and B respectively, which are mutually perpendicular to each other. Which one of the following gives the condition for which the particle moves undeflected in its original trajectory?
A very high magnetic field is applied to a stationary charge. Then the charge experiences ______.
A solenoid 60 cm long and of radius 4.0 cm has 3 layers of windings of 300 turns each. A 2.0 cm long wire of mass 2.5 g lies inside the solenoid (near its centre) normal to its axis; both the wire and the axis of the solenoid are in the horizontal plane. The wire is connected through two leads parallel to the axis of the solenoid to an external battery which supplies a current of 6.0 A in the wire. What value of current (with appropriate sense of circulation) in the windings of the solenoid can support the weight of the wire? (g = 9.8 m s–2)
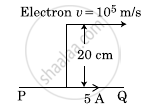
An infinitely long straight conductor carries a current of 5 A as shown. An electron is moving with a speed of 105 m/s parallel to the conductor. The perpendicular distance between the electron and the conductor is 20 cm at an instant. Calculate the magnitude of the force experienced by the electron at that instant.
What is the relation between Tesla and Gauss?
