Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An electron enters with a velocity v = v0i into a cubical region (faces parallel to coordinate planes) in which there are uniform electric and magnetic fields. The orbit of the electron is found to spiral down inside the cube in plane parallel to the x-y plane. Suggest a configuration of fields E and B that can lead to it.
Solution
Due to magnetic force charge particle revolves in uniform circular motion in x-y plane and due to electric field charge particle increases the speed along the x-direction, which in turn increases the radius of circular path and hence, particle traversed on spiral path.
Let us consider a magnetic field B = B0 present in the region and an electron enters with a velocity into cubical region (faces parallel to coordinate planes). The force on the electron, using magnetic Lorentz force, is given by
The velocity of electron is v = v0i, i.e., along X-axis as magnetic field is perpendicular to velocity so it is in Y-direction.
The moving electron enters into cubical region. The force on electron due to Lorentz force
F = q(E + v × B)
By putting the values
Fm = `-e[v_ohati xx bhatk] = -ev_0Bhatj`
Which revolves around the electron in X-Y plane.
The force due to electric field `F_m = evecKhatk` accelerates electron along z-axis and force due to magnetic field keeps it in circular motion, which in turn increases the radius of circular path. So the motion becomes helical path.
Which revolves the electron in x-y plane.
The electric force F = eE0j accelerates e along the z-axis which in turn increases the radius of circular path and hence particle traversed on spiral path.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A long straight wire carries a current of 35 A. What is the magnitude of the field B at a point 20 cm from the wire?
A horizontal overhead power line carries a current of 90 A in east to west direction. What is the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field due to the current 1.5 m below the line?
State whether the following statement is true or false:
Magnetic poles exist in pairs.
A proton enters into a magnetic field of induction 1.732 T, with a velocity of 107 m/s at an angle 60° to the field. The force acting on the proton is e = 1.6 × 10-19 C, sin 60° = cos 30° = `sqrt3/2`
The magnetic moment of a current I carrying circular coil of radius r and number of turns N varies as ______.
Which one of the following is a correct statement about magnetic forces?
A magnetic field exerts no force on
A cubical region of space is filled with some uniform electric and magnetic fields. An electron enters the cube across one of its faces with velocity v and a positron enters via opposite face with velocity – v. At this instant ______.
- the electric forces on both the particles cause identical accelerations.
- the magnetic forces on both the particles cause equal accelerations.
- both particles gain or loose energy at the same rate.
- the motion of the centre of mass (CM) is determined by B alone.
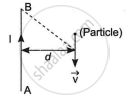
A long straight wire AB carries a current I. A particle (mass m and charge q) moves with a velocity `vec"v"`, parallel to the wire, at a distance d from it as shown in the figure. Obtain the expression for the force experienced by the particle and mention its directions.