Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A cubical region of space is filled with some uniform electric and magnetic fields. An electron enters the cube across one of its faces with velocity v and a positron enters via opposite face with velocity – v. At this instant ______.
- the electric forces on both the particles cause identical accelerations.
- the magnetic forces on both the particles cause equal accelerations.
- both particles gain or loose energy at the same rate.
- the motion of the centre of mass (CM) is determined by B alone.
Options
a, b and c
a, c and d
b, c and d
c and d
Solution
b, c and d
Explanation:
This problem is based upon the single moving charge placed with some uniform electric and magnetic fields in space. Then they experience a force called Lorentz force given by the relation Fnet = qE + q(v × B).
- The magnetic forces (Fm = q(v × B)), on charge particle is either zero or Fm is perpendicular to v (or component of v) which in turn revolves particles on a circular path with uniform speed. In both cases, particles have equal accelerations.
- Due to the same electric force (Fe = qE) which is in opposite direction (because of the sign of charge) both the particles gain or loss energy at the same rate.
- There is no change of the Centre of Mass (CM) of the particles, therefore the motion of the Centre of Mass (CM) is determined by B alone.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Magnetic lines of force always cross each other
A charge ‘q’ moving along the X- axis with a velocity `vecv` is subjected to a uniform magnetic field B along the Z-axis as it crosses the origin O.
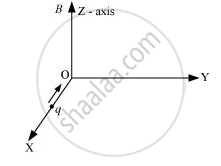
(i) Trace its trajectory.
(ii) Does the charge gain kinetic energy as it enters the magnetic field? Justify your answer.
Two wires carrying equal currents i each, are placed perpendicular to each other, just avoiding a contact. If one wire is held fixed and the other is free to move under magnetic forces, what kind of motion will result?
A particle of charge -16 x 10-18 C moving with velocity 10 m/s along the X-axis enters a region where a magnetic field of induction B is along Y-axis and electric field of magnitude 104 V/m is along the negative Z-axis. If the charged particle continues moving along the X-axis, the magnitude of B is ____________.
The magnetic moment of a current I carrying circular coil of radius r and number of turns N varies as ______.
A circular current loop of magnetic moment M is in an arbitrary orientation in an external magnetic field B. The work done to rotate the loop by 30° about an axis perpendicular to its plane is ______.
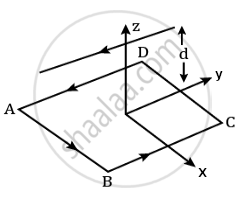
Figure shows a square loop. 20 cm on each side in the x-y plane with its centre at the origin. The loop carries a current of 7 A. Above it at y = 0, z = 12 cm is an infinitely long wire parallel to the x axis carrying a current of 10 A. The net force on the loop is ______ × 10-4 N.
A unit vector is represented as `(0.8hat"i" + "b"hat"j" + 0.4hat"k")`. Hence the value of 'b' must be ______.
With a neat labelled diagram, explain cyclotron motion and cyclotron formula.
