Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Two wires carrying equal currents i each, are placed perpendicular to each other, just avoiding a contact. If one wire is held fixed and the other is free to move under magnetic forces, what kind of motion will result?
Solution
The magnetic force on a wire carrying an electric current i is \[\vec{F} = i . ( \vec{l} \times \vec{B} )\] , where l is the length of the wire and B is the magnetic field acting on it. Suppose we have one wire in the horizontal direction (fixed) and other wire in the vertical direction (free to move). If the horizontal wire is carrying current from right to left is held fixed perpendicular to the vertical wire, which is free to move, the upper portion of the free wire will tend to move in the left direction and the lower portion of the wire will tend to move in the right direction, according to Fleming's left hand rule, as the magnetic field acting on the wire due to the fixed wire will point into the plane of paper above the wire and come out of the paper below the horizontal wire and the current will flow in upward direction in the free wire. Thus, the free wire will tend to become parallel to the fixed wire so as to experience maximum attractive force.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A rod of length l is moved horizontally with a uniform velocity 'v' in a direction perpendicular to its length through a region in which a uniform magnetic field is acting vertically downward. Derive the expression for the emf induced across the ends of the rod.
A circular coil of wire consisting of 100 turns, each of radius 8.0 cm carries a current of 0.40 A. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the centre of the coil?
A long straight wire carries a current of 35 A. What is the magnitude of the field B at a point 20 cm from the wire?
A particle of charge ‘q’ and mass ‘m’ is moving with velocity .`vecV` It is subjected to a uniform magnetic field `vecB` directed perpendicular to its velocity. Show that it describes a circular path. Write the expression for its radius.
The free electrons in a conducting wire are in constant thermal motion. If such a wire, carrying no current, is placed in a magnetic field, is there a magnetic force on each free electron? Is there a magnetic force on the wire?
A charged particle is moved along a magnetic field line. The magnetic force on the particle is
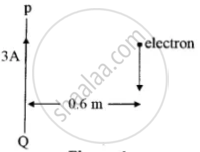
PQ is a long straight conductor carrying a current of 3A as shown in Figure below. An electron moves with a velocity of 2 x 107 ms-1 parallel to it. Find the force acting on the electron.
A proton enters into a magnetic field of induction 1.732 T, with a velocity of 107 m/s at an angle 60° to the field. The force acting on the proton is e = 1.6 × 10-19 C, sin 60° = cos 30° = `sqrt3/2`
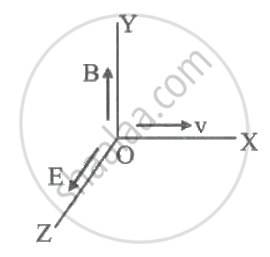
A particle of charge -16 x 10-18 C moving with velocity 10 m/s along the X-axis enters a region where a magnetic field of induction B is along Y-axis and electric field of magnitude 104 V/m is along the negative Z-axis. If the charged particle continues moving along the X-axis, the magnitude of B is ____________.
For a circular coil of radius R and N turns carrying current I, the magnitude of the magnetic field at a point on its axis at a distance x from its centre is given by,
B = `(μ_0"IR"^2"N")/(2("x"^2 + "R"^2)^(3/2))`
(a) Show that this reduces to the familiar result for field at the centre of the coil.
(b) Consider two parallel co-axial circular coils of equal radius R, and number of turns N, carrying equal currents in the same direction, and separated by a distance R. Show that the field on the axis around the mid-point between the coils is uniform over a distance that is small as compared to R, and is given by, B = `0.72 (μ_0"NI")/"R"` approximately.
[Such an arrangement to produce a nearly uniform magnetic field over a small region is known as Helmholtz coils.]
A magnetic field set up using Helmholtz coils is uniform in a small region and has a magnitude of 0.75 T. In the same region, a uniform electrostatic field is maintained in a direction normal to the common axis of the coils. A narrow beam of (single species) charged particles all accelerated through 15 kV enters this region in a direction perpendicular to both the axis of the coils and the electrostatic field. If the beam remains undeflected when the electrostatic field is 9.0 × 10–5 V m–1, make a simple guess as to what the beam contains. Why is the answer not unique?
Lorentz Force generally refers to ______.
Which one of the following is a correct statement about magnetic forces?
A magnetic field exerts no force on
Consider a wire carrying a steady current, I placed in a uniform magnetic field B perpendicular to its length. Consider the charges inside the wire. It is known that magnetic forces do no work. This implies that ______.
- motion of charges inside the conductor is unaffected by B since they do not absorb energy.
- some charges inside the wire move to the surface as a result of B.
- if the wire moves under the influence of B, no work is done by the force.
- if the wire moves under the influence of B, no work is done by the magnetic force on the ions, assumed fixed within the wire.
A charge particle moves along circular path in a uniform magnetic field in a cyclotron. The kinetic energy of the charge particle increases to 4 times its initial value. What will be the ratio of new radius to the original radius of circular path of the charge particle:
A beam of light travelling along X-axis is described by the electric field Ey = 900 sin ω(t - x/c). The ratio of electric force to magnetic force on a charge q moving along Y-axis with a speed of 3 × 107 ms-1 will be : [Given speed of light = 3 × 108 ms-1]
A long straight conductor kept along X' X axis, carries a steady current I along the +x direction. At an instant t, a particle of mass m and charge q at point (x, y) moves with a velocity `vecv` along +y direction. Find the magnitude and direction of the force on the particle due to the conductor.
With a neat labelled diagram, explain cyclotron motion and cyclotron formula.
