Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The free electrons in a conducting wire are in constant thermal motion. If such a wire, carrying no current, is placed in a magnetic field, is there a magnetic force on each free electron? Is there a magnetic force on the wire?
Solution
As the electrons are in motion, there is a magnetic force acting on them individually. But the current through the wire represents the collective motion of all the electrons that are moving or vibrating very randomly; so, overall effect is negligible. Hence there is no net magnetic force on the wire.
Also, F = LLB sin (θ)
So, if the current in the wire is zero, then the force experienced by the wire will also be zero.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Two long, straight, parallel conductors carry steady currents, I1 and I2, separated by a distance d. If the currents are flowing in the same direction, show how the magnetic field set up in one produces an attractive force on the other? Obtain the expression for this force. Hence, define one ampere.
A horizontal overhead power line carries a current of 90 A in east to west direction. What is the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field due to the current 1.5 m below the line?
Obtain an expression for magnetic flux density B at the centre of a circular coil of radius R, having N turns and carrying a current I
Define one tesla using the expression for the magnetic force acting on a particle of charge q moving with velocity \[\vec{v}\] in a magnetic field \[\vec{B}\] .
A circular coil of N turns and radius R carries a current I. It is unwound and rewound to make another coil of radius R/2, current I remaining the same. Calculate the ratio of the magnetic moments of the new coil and original coil.
A charge ‘q’ moving along the X- axis with a velocity `vecv` is subjected to a uniform magnetic field B along the Z-axis as it crosses the origin O.
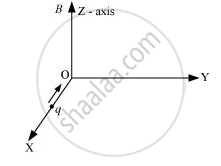
(i) Trace its trajectory.
(ii) Does the charge gain kinetic energy as it enters the magnetic field? Justify your answer.
A straight horizontal wire of mass 10 mg and length 1.0 m carries a current of 2.0 A. What minimum magnetic field B should be applied in the region, so that the magnetic force on the wire may balance its weight?
PQ is a long straight conductor carrying a current of 3A as shown in Figure below. An electron moves with a velocity of 2 x 107 ms-1 parallel to it. Find the force acting on the electron.
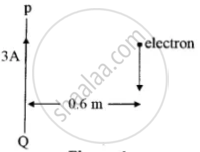
Explain "Magnetic force never does any work on moving charges".
Show that currents in two long, straight, parallel wires exert forces on each other. Derive the expression for the force per unit length on each conductor.
For a circular coil of radius R and N turns carrying current I, the magnitude of the magnetic field at a point on its axis at a distance x from its centre is given by,
B = `(μ_0"IR"^2"N")/(2("x"^2 + "R"^2)^(3/2))`
(a) Show that this reduces to the familiar result for field at the centre of the coil.
(b) Consider two parallel co-axial circular coils of equal radius R, and number of turns N, carrying equal currents in the same direction, and separated by a distance R. Show that the field on the axis around the mid-point between the coils is uniform over a distance that is small as compared to R, and is given by, B = `0.72 (μ_0"NI")/"R"` approximately.
[Such an arrangement to produce a nearly uniform magnetic field over a small region is known as Helmholtz coils.]
- If v is parallel to B, then path of particle is spiral.
- If v is perpendicular to B, then path of particle is a circle.
- If v has a component along B, then path of particle is helical.
- If v is along B, then path of particle is a circle.
- perpendicular to direction of velocity of charged particle.
-
perpendicular to direction of magnetic field.
-
parallel to direction of velocity of charged particle.
-
parallel to the direction of magnetic field.
The correct plot of the magnitude of magnetic field `vec"B"` vs distance r from centre of the wire is, if the radius of wire is R.
The phenomenon in which a magnetic field is produced in the space near a conductor carrying current is called ______
Consider a wire carrying a steady current, I placed in a uniform magnetic field B perpendicular to its length. Consider the charges inside the wire. It is known that magnetic forces do no work. This implies that ______.
- motion of charges inside the conductor is unaffected by B since they do not absorb energy.
- some charges inside the wire move to the surface as a result of B.
- if the wire moves under the influence of B, no work is done by the force.
- if the wire moves under the influence of B, no work is done by the magnetic force on the ions, assumed fixed within the wire.
Show that a force that does no work must be a velocity dependent force.
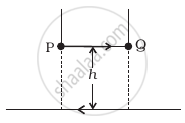
A long straight wire carrying current of 25 A rests on a table as shown in figure. Another wire PQ of length 1 m, mass 2.5 g carries the same current but in the opposite direction. The wire PQ is free to slide up and down. To what height will PQ rise?
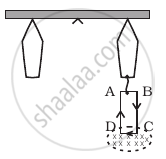
A 100 turn rectangular coil ABCD (in XY plane) is hung from one arm of a balance (Figure). A mass 500 g is added to the other arm to balance the weight of the coil. A current 4.9 A passes through the coil and a constant magnetic field of 0.2 T acting inward (in xz plane) is switched on such that only arm CD of length 1 cm lies in the field. How much additional mass ‘m’ must be added to regain the balance?
The unit Wbm-2 is equal to ______.
