Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A long straight conductor kept along X' X axis, carries a steady current I along the +x direction. At an instant t, a particle of mass m and charge q at point (x, y) moves with a velocity `vecv` along +y direction. Find the magnitude and direction of the force on the particle due to the conductor.
Solution
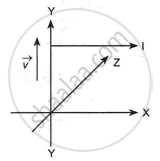
From relation,
`vecF = qvB[(-hati) xx (hatk)]`
`vecF = qvBhatj`
According to Fleming's left-hand rule, the magnetic field will point in a direction that is (x) inside the paper's plane. Therefore, the force will be applied in the conductor's direction of travel. Therefore, the force will be exerted in the +y direction.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Two long, straight, parallel conductors carry steady currents, I1 and I2, separated by a distance d. If the currents are flowing in the same direction, show how the magnetic field set up in one produces an attractive force on the other? Obtain the expression for this force. Hence, define one ampere.
A charged particle is moved along a magnetic field line. The magnetic force on the particle is
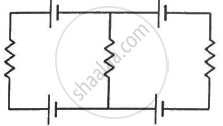
Each of the batteries shown in figure has an emf equal to 5 V. Show that the magnetic field B at the point P is zero for any set of values of the resistances.
Choose the correct alternative and rewrite the following:
What will happen to the current passing through a resistance, if the potential difference across it is doubled and the resistance is halved?
Lorentz Force generally refers to ______.
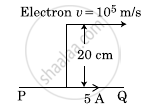
An infinitely long straight conductor carries a current of 5 A as shown. An electron is moving with a speed of 105 m/s parallel to the conductor. The perpendicular distance between the electron and the conductor is 20 cm at an instant. Calculate the magnitude of the force experienced by the electron at that instant.
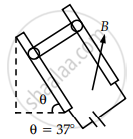
A 100 turn rectangular coil ABCD (in XY plane) is hung from one arm of a balance (Figure). A mass 500 g is added to the other arm to balance the weight of the coil. A current 4.9 A passes through the coil and a constant magnetic field of 0.2 T acting inward (in xz plane) is switched on such that only arm CD of length 1 cm lies in the field. How much additional mass ‘m’ must be added to regain the balance?
At a certain place the angle of dip is 30° and the horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field is 0.5 G. The earth’s total magnetic field (in G), at that certain place, is ______.
Two conducting rails are connected to a source of emf and form an incline as shown in figure. A bar of mass 50 g slides without friction down the incline through a vertical magnetic field B. If the length of the bar is 50 cm and a current of 2.5 A is provided by battery. Value of B for which the bar slide at a constant velocity ______ × 10-1 Tesla. 2 [g = 10 m/s2]