Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Choose the correct alternative and rewrite the following:
What will happen to the current passing through a resistance, if the potential difference across it is doubled and the resistance is halved?
Options
remains unchanged
becomes double
becomes half
becomes four times
Solution
becomes four times
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
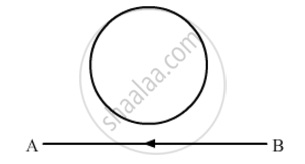
The electric current flowing in a wire in the direction from B to A is decreasing. Find out the direction of the induced current in the metallic loop kept above the wire as shown.
A steady current (I1) flows through a long straight wire. Another wire carrying steady current (I2) in the same direction is kept close and parallel to the first wire. Show with the help of a diagram how the magnetic field due to the current I1 exerts a magnetic force on the second wire. Write the expression for this force.
The free electrons in a conducting wire are in constant thermal motion. If such a wire, carrying no current, is placed in a magnetic field, is there a magnetic force on each free electron? Is there a magnetic force on the wire?
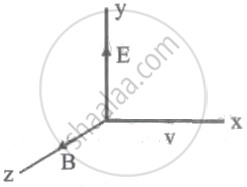
A particle with charge q moves with a velocity v in a direction perpendicular to the directions of uniform electric and magnetic fields, E and B respectively, which are mutually perpendicular to each other. Which one of the following gives the condition for which the particle moves undeflected in its original trajectory?
A very high magnetic field is applied to a stationary charge. Then the charge experiences ______.
For a circular coil of radius R and N turns carrying current I, the magnitude of the magnetic field at a point on its axis at a distance x from its centre is given by,
B = `(μ_0"IR"^2"N")/(2("x"^2 + "R"^2)^(3/2))`
(a) Show that this reduces to the familiar result for field at the centre of the coil.
(b) Consider two parallel co-axial circular coils of equal radius R, and number of turns N, carrying equal currents in the same direction, and separated by a distance R. Show that the field on the axis around the mid-point between the coils is uniform over a distance that is small as compared to R, and is given by, B = `0.72 (μ_0"NI")/"R"` approximately.
[Such an arrangement to produce a nearly uniform magnetic field over a small region is known as Helmholtz coils.]
Assertion: Free electrons always keep on moving in a conductor even then no magnetic force act on them in magnetic field unless a current is passed through it.
Reason: The average velocity of free electron is zero.
A deuteron of kinetic energy 50 keV is describing a circular orbit of radius 0.5 metre in a plane perpendicular to the magnetic field B. The kinetic energy of the proton that describes a circular orbit of radius 0.5 metre in the same plane with the same B is ______.
The correct plot of the magnitude of magnetic field `vec"B"` vs distance r from centre of the wire is, if the radius of wire is R.
A magnetic field exerts no force on
The phenomenon in which a magnetic field is produced in the space near a conductor carrying current is called ______
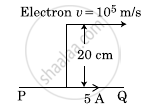
An infinitely long straight conductor carries a current of 5 A as shown. An electron is moving with a speed of 105 m/s parallel to the conductor. The perpendicular distance between the electron and the conductor is 20 cm at an instant. Calculate the magnitude of the force experienced by the electron at that instant.
Two charged particles traverse identical helical paths in a completely opposite sense in a uniform magnetic field B = B0k̂.
A cubical region of space is filled with some uniform electric and magnetic fields. An electron enters the cube across one of its faces with velocity v and a positron enters via opposite face with velocity – v. At this instant ______.
- the electric forces on both the particles cause identical accelerations.
- the magnetic forces on both the particles cause equal accelerations.
- both particles gain or loose energy at the same rate.
- the motion of the centre of mass (CM) is determined by B alone.
A charged particle of charge e and mass m is moving in an electric field E and magnetic field B. Construct dimensionless quantities and quantities of dimension [T]–1.
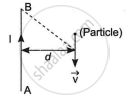
A long straight wire AB carries a current I. A particle (mass m and charge q) moves with a velocity `vec"v"`, parallel to the wire, at a distance d from it as shown in the figure. Obtain the expression for the force experienced by the particle and mention its directions.
With a neat labelled diagram, explain cyclotron motion and cyclotron formula.
State dimensions of magnetic field.
