Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Choose the correct alternative and rewrite the following:
Mirror used by a dental surgeon is ..........................
Options
plane
convex
concave
convex and concave
Solution
concave
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A student used a device (X) to obtain/focus the image of a well illuminated distant building on a screen (S) as shown below in the diagram. Select the correct statement about the device (X).

Define the following term in the context of spherical mirrors:- Principal focus
Explain the following term related to spherical lenses:- aperture
Explain the following term related to spherical lenses:- principal focus
Image formed by a convex ______ is always virtual and smaller in size.
An image formed by a ______ mirror is always of the same size as that of the object.
We can obtain a real, enlarged and inverted image by a concave mirror.
A concave mirror always forms a real image.
Match the items given in Column I with one or more items of Column II.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (a) | A plane mirror | (i) | Used as a magnifying glass. |
| (b) | A convex mirror | (ii) | Can form image of objects spread over a large area. |
| (c) | A convex lens | (iii) | Used by dentists to see enlarged image of teeth. |
| (d) | A concave mirror | (iv) | The image is always inverted and magnified. |
| (e) | A concave lens | (v) | The image is erect and of the same size as the object. |
| (vi) | The image is erect and smaller in size than the object. |
Find out the letters of English alphabet or any other language known to you in which the image formed in a plane mirror appears exactly like the letter itself. Discuss your findings.
What is a virtual image?
Give one use each of a concave and a convex mirror.
Name the spherical mirror which has:
(a) virtual principal focus.
(b) real principal focus.
When a spherical mirror is held towards the sun and its sharp image is formed on a piece of a carbon paper for some time, a hole is burnt in the carbon paper.
What is the nature of spherical mirror?
When a spherical mirror is held towards the sun and its sharp image is formed on a piece of a carbon paper for some time, a hole is burnt in the carbon paper.
What name is given to the distance between spherical mirror and carbon paper?
Write the mirror formula. Give the meaning of each symbol which occurs in it.
Name the spherical mirror which can produce a real and diminished image of an object.
State the kind of mirror used
(a) by a dentist, and
(b) as a street light reflector.
AB and CD, two spherical mirrors, from parts of a hollow spherical ball with its centre at O as shown in the diagram. If arc AB = `1/2` arc CD, what is the ratio of their focal lengths? State which of the two mirrors will always form virtual image of an object placed in front of it and why.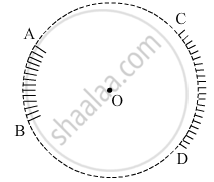
State the two convenient rays that are chosen to construct the image by a spherical mirror for a given object? Explain your answer with the help of suitable ray diagrams.
How will you distinguish between a plane mirror, a concave mirror and a convex mirror, without touching them?
The image formed by a convex mirror is
An object 5 cm high is placed at a distance 60 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. Find the position and size of the image.
The sun is seen before the sunrise and after the sunset.
Define the following term in relation to concave mirror.
Center of curvature
What is the relation between focal length and radius of curvature of a concave mirror?
Define the term Principal axis.
Define the term Principal focus.
An object 10 cm high is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a spherical mirror of focal length 25 cm. By scale drawing find the nature, position, and magnification of the image in the following case:
Convex mirror
The following Figure shows a concave mirror MM' on which a ray of light incident from a point P gets reflected to meet the principle axis at O.
(a) Find, by construction, the position of the centre of curvature of the concave mirror.
(b) Write down the value for the radius of curvature of the mirror.
(c) Calculate the focal length of the mirror.
(d ) Which relation is used in deducing the focal length from the radius of curvature?
The distance from the pole to the focus is called ______.
Explain why a ray of light passing through the center of curvature of a concave mirror, gets reflected along with the same pattern.
What is “aperture”?
