Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Name the spherical mirror which can produce a real and diminished image of an object.
Solution
Only a concave mirror can produce a real and diminished image of an object.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain the following term related to spherical lenses:- principal axis
Explain the following term related to spherical lenses:- principal focus
Define Radius of curvature of the spherical mirror
Define (a) centre of curvature (b) radius of curvature (c) pole (d) principal axis, and (e) aperture, of a spherical mirror with the help of a labelled diagram
A concave lens produces an image 20 cm from the lens of an object placed 30 cm from the lens. The focal length of the lens is:
(a) 50 cm
(b) 40 cm
(c) 60 cm
(d) 30 cm
State the kind of mirror used
(a) by a dentist, and
(b) as a street light reflector.
State the number of images of an object placed between two mirrors, formed in each case when mirrors are inclined to each other at (a) 90°, and (b) 60°.
Draw suitable diagrams to illustrate the action of (i) concave mirror and (ii) convex mirror on a beam of light incident parallel to the principal axis.
State the two convenient rays that are chosen to construct the image by a spherical mirror for a given object? Explain your answer with the help of suitable ray diagrams.
Figure shows a concave mirror with its pole at P, focus F and centre of curvature C. Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object OA.
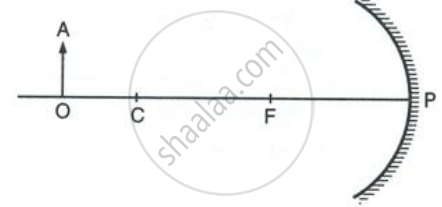
For what position of object, the image formed by a concave mirror is magnified and erect?
The radius of curvature of a convex mirror is 40 cm. Find its focal length.
A concave mirror forms a virtual image of size twice that of the object placed at a distance 5 cm from it.
Find : (a) the focal length of the mirror (b) position of image
Answer the following question.
Write the modification in the curvature of the eye lens which enables us to see the nearby objects clearly?
Draw a ray diagram to show that a convex mirror has a wider field of view.
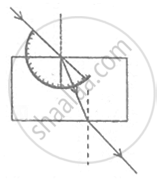
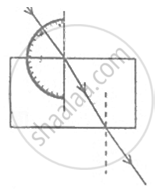
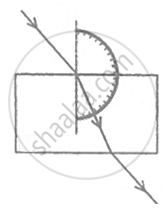
A student traces the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular slab.
 |
 |
 |
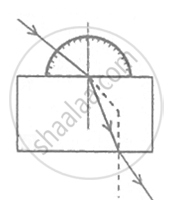 |
For measuring the angle of incidence, he must position the protractor in the manner shown in the figure:
