Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
![Frank solutions for Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 6 - Light Frank solutions for Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 6 - Light - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-9-icse_6:1a0f7706074c4feda1fb5ca0ff12ac66.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 6: Light
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 6 of CISCE Frank for Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE.
Frank solutions for Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 6 Light Reflection of Light [Pages 245 - 247]
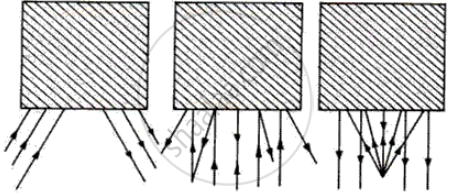
Identify the following kind of beam of light.

Identify the following kind of beam of light.
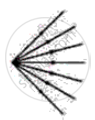
Identify the following kind of beam of light.
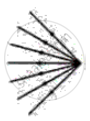
Identify the following kind of beam of light.

Out of the following, choose the substance which is translucent medium:
Wood
water
waxed paper
stone
black paper
State the laws of reflection.
The angle between an incident ray and the mirror is 350.
(i) What is the angle of incidence?
(ii) What is the angle of reflection?
(iii) What is the total angle turned by the ray of light?
(iv) What is the angle between the incident and the reflected rays?
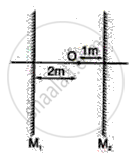
A boy is standing in front of a plane mirror at a distance of 3 m from it.
(i) What is the distance between the boy and his image?
(ii) If the boy moves 1 m backward, find the distance between the image and the boy.
The reflection of a ray of light (OA) normally incident on a plane mirror is shown below
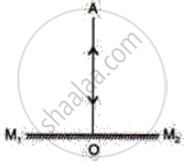
What are the angles of incidence and reflection?
Draw two sets of rays of light to show the formation of an image of the letter as shown in figure p.

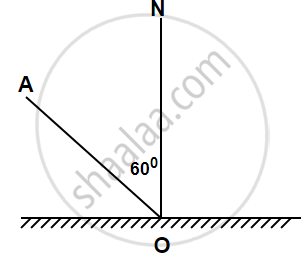
Show an incident ray AO and the normal ON a plan mirror. draw the reflected ray and then find the angle between the incident and reflected rays.
Frank solutions for Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 6 Light Spherical Mirrors [Page 258]
Define the term Pole.
Define the term Centre of curvature.
Define the term Aperture.
Define the term Principal axis.
Define the term Principal focus.
What is the relationship between the focal length and radius of curvature?
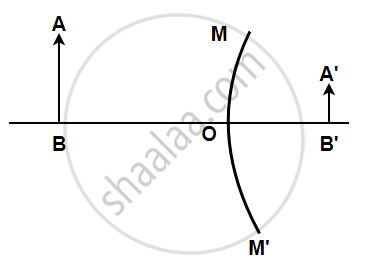
AB is the object, A1B1 is its image. MM' is the position of the mirror. Complete the ray diagram and find the position of the center of curvature and focus of the mirror. Also, measure the focal length.
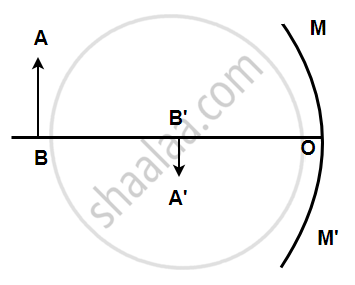
AB is the object, A'B' is the image, and MM' is the position of the mirror. Complete the ray diagram showing the formation of the image and find the focal length of the mirror.
Complete the following diagrams shown in the following figures by drawing the reflected rays.

Complete the following diagrams shown in the following figures by drawing the reflected rays.
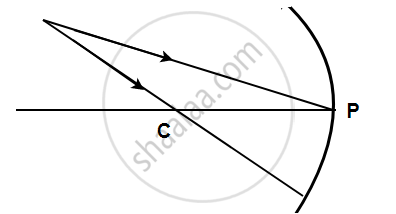
Complete the following diagrams shown in the below figure by drawing the reflected ray for each incident ray.
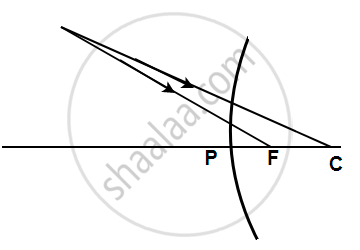
Complete the following diagrams shown in the below figure by drawing the reflected ray for each incident ray.
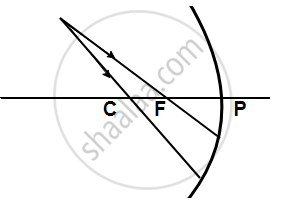
The following figure shows a concave mirror with its pole (P), focus (F), and center of curvature (C). Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image of an object AB by the concave mirror.
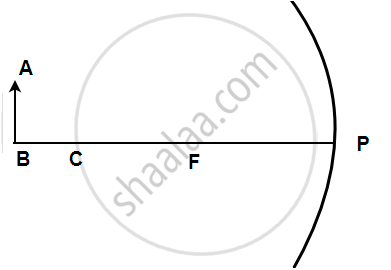
In the following figure shows a concave mirror with its pole (P), focus (F) and centre of curvature (C). Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image of an object AB by the concave mirror.
Frank solutions for Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 6 Light Exercise [Pages 261 - 264]
Name the spherical mirror which can produce a real and diminished image of an object.
What is a mirror formula?
Define linear magnification produced by a mirror?
Find the height of the image of a body of height 1.5m in a mirror with a magnification of 1.5.
The boxes in figure (a, b, c) represent mirrors; insert a mirror which will reflect the incident ray as shown in the diagram.
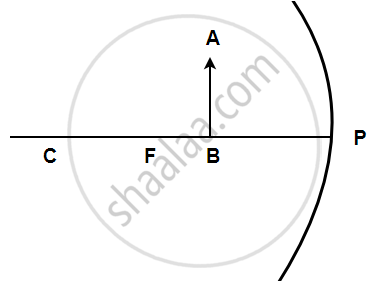
Give two uses of convex mirror.
State whether the following statement is true or false. If false, correct it.
The angle of incidence is the angle made by the incident ray with the plane mirror.
True
False
State whether the following statement is true or false. If false, correct it.
If a ray of light incident on a plane mirror is such that it makes an angle of 30o with the mirror, then the angle of reflection is 60o.
True
False
State whether the following statement is true or false. If false, correct it.
If the incident ray makes an angle of Xo with the normal, then the reflected ray is 2Xo.
True
False
State whether the following statement is true or false. If false, correct it.
The image in a plane mirror is situated in the mirror.
True
False
State whether the following statement is true or false. If false, correct it.
The image formed in a plane mirror is the real, erect, and same size as that of the object.
True
False
When a ray of light strikes a plane mirror at an angle of 150 with the mirror, what will be the angle through which the ray will deviate? Illustrate with a ray diagram in the following figure.

The word PLATE written on a paper is held in front of a plane mirror. Write down the letters as seen in the following case.
The paper is held parallel to the mirror.
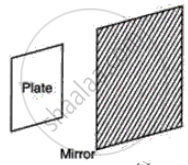
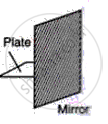
The word PLATE written on a paper is held in front of a plane mirror. Write down the letters as seen in the following case.
The paper is held perpendicular to the mirror.
A boy is standing in front of a plane mirror at a distance of 3 m from it.
(i) What is the distance between the boy and his image?
(ii) If the boy moves 1 m backward, find the distance between the image and the boy.
Complete the ray diagram to show the image observed by the eye after reflection in the following figure.
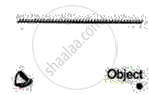
Complete the ray diagram to show the image observed by the eye after reflection in the following figure.

Define the term Pole.
Define the term Centre of curvature.
Define the term Principle focus.
Define the term Principle axis.
Define the term Focus of a concave mirror.
Define the term Normal.
Locate the image termed when the object is placed between two planes as shown in the following figure.
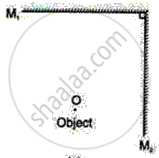
Locate the image termed when the object is placed between two planes as shown in the following figure.
Complete the path of incident ray in the following case.

Complete the path of incident ray in the following case.
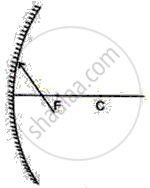
Complete the path of incident ray in the following case.
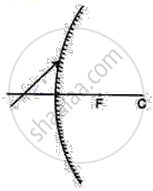
By geometrical construction, find the position of the image in the following figure.
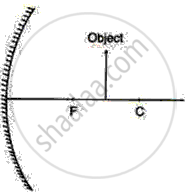
An object is placed in front of a convex mirror of focal length 25 cm. By scale, a drawing shows the formation of image and states the nature of image.
Given that v = 10 cm.
Draw a ray diagram to show that a convex mirror has a wider field of view.
A concave mirror can be used to produce a parallel beam of light. Draw a ray to illustrate this.
An object 10 cm high is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a spherical mirror of focal length 25 cm. By scale drawing find the nature, position, and magnification of the image in the following case:
Concave mirror
An object 10 cm high is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a spherical mirror of focal length 25 cm. By scale drawing find the nature, position, and magnification of the image in the following case:
Convex mirror
An object is placed in front of a concave mirror as shown in the following figure. By scale drawing, find the nature of the image. Given f = 10 cm, v = 30 cm.
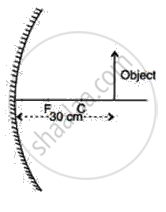
The following Figure shows a concave mirror MM' on which a ray of light incident from a point P gets reflected to meet the principle axis at O.
(a) Find, by construction, the position of the centre of curvature of the concave mirror.
(b) Write down the value for the radius of curvature of the mirror.
(c) Calculate the focal length of the mirror.
(d ) Which relation is used in deducing the focal length from the radius of curvature?
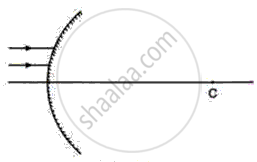
The diagram below shows the parallel rays incident on a convex mirror. C is the centre of the curvature of the mirror. By drawing the paths of the reflected rays, label the focus F and hence find the focal length of the mirror.
Solutions for 6: Light
![Frank solutions for Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 6 - Light Frank solutions for Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 6 - Light - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-9-icse_6:1a0f7706074c4feda1fb5ca0ff12ac66.jpg)
Frank solutions for Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 6 - Light
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Frank solutions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE 6 (Light) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Frank textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 6 Light are Rules for the Construction of Image Formed by a Spherical Mirror, Focus and Focal Length, Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors, Concave Mirror, Image Formation by Concave Mirror, Convex Mirror, Mirror Equation/Formula, Images Formed by a Plane Mirrors, Distinction Between a Plane Mirror, Concave Mirror and Convex Mirror, Images Formed in a Pair of Mirrors Placed Parallel to Each Other, Images Formed by Two Mirrors Placed Perpendicular to Each Other, Spherical Mirrors, Image Formation by Convex Mirror, Relationship Between the Focal Length and Radius of Curvature, Sign Convention, Reflection of Light, Types of Reflection, Terms Used in Reflection of Light, Law of Reflection of Light, Verification of the Law of Reflection of Light, Formation of Image by Reflection: Real and Virtual Image, Formation of Image of a Point Object by a Plane Mirror, Image of an Extended Object Formed by a Plane Mirror, Position of Image, Lateral Inversion, Plane Mirror, Images Formed in Two Inclined Mirrors.
Using Frank Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE solutions Light exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Frank Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE students prefer Frank Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 6, Light Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
