Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Complete the following diagrams shown in the below figure by drawing the reflected ray for each incident ray.
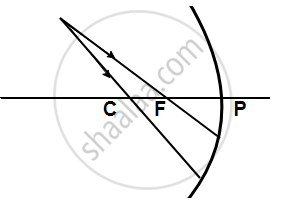
Solution
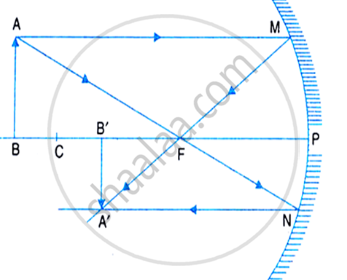
A light ray coming from a point on object AB passes through the principal focus and after reflection, it becomes parallel to the principal axis in accordance with laws of reflection and the other ray passing through the centre of curvature strikes the mirror normally i.e. 90 degrees. Hence it will reflect back. These two reflected rays coincide at a point where the image is formed. The image, A'B' is real, inverted, and diminished in size.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What do you mean by the term dispersion?
Which are the two convenient rays that are chosen to construct the image by a spherical mirror for a given object? Explain with the help of suitable ray diagrams.
Name the kind of mirror used to obtain :
A real and enlarged image
A concave mirror forms a virtual image of size twice that of the object placed at a distance 5 cm from it.
Find : (a) the focal length of the mirror (b) position of image
Define the following term in relation to concave mirror.
Center of curvature
Define the following term in relation to concave mirror.
Focal length
Find the height of the image of a body of height 1.5m in a mirror with a magnification of 1.5.
Numerical problem.
The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 25 cm. Find its focal length.
If the real image of a candle flame formed by a lens is three times the size of the flame and the distance between lens and image is 80 cm, at what distance should the candle be placed from the lens?
