Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Complete the following diagrams shown in the below figure by drawing the reflected ray for each incident ray.
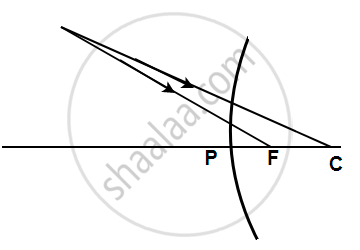
Solution
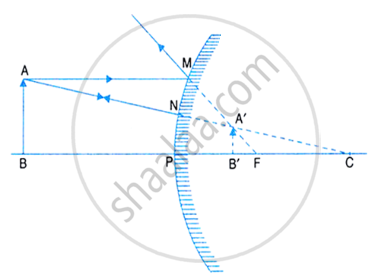
A light ray when produced backwards passes through principal focus as shown in the problem figure. We draw the normal through the centre of curvature at the point of incidence and draw the reflected ray at an angle equal to the angle of incidence thus following the laws of reflection. The reflected ray is parallel to the principal axis. The other ray is passing through the centre of curvature as shown in the problem figure. This ray retraces its incident path because it strikes the mirror normally i.e. 90 degrees. These two reflected rays when produced backwards coincide at a point where the image is formed. The image, A'B' is virtual, erect, and diminished in size.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When a spherical mirror is held towards the sun and its sharp image is formed on a piece of a carbon paper for some time, a hole is burnt in the carbon paper.
At which point of the spherical mirror the carbon paper is placed?
The shiny outer surface of a hollow sphere of aluminium of radius 50 cm is to be used as a mirror:
What will be the focal length of this mirror?
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a concave mirror for the object beyond its centre of curvature. State three characteristics of the image.
For what position of object, the image formed by a concave mirror is magnified and erect?
When an object of height 1 cm is kept at a distance 4 cm from a concave mirror, its erect image of height 1.5 cm is formed at a distance 6 cm behind the mirror. Find the focal length of mirror, by drawing.
Draw a ray diagram in each of the following cases to show the formation of image, when the object is placed :
(i) between the optical centre and principal focus of a convex lens.
(ii) anywhere in front of a concave lens.
(iii) at 2F of a convex lens.
State the signs and values of magnifications in the above-mentioned cases (i) and (ii).
Select the correct option:
A concave mirror is made by cutting a portion of a hollow glass sphere of radius 30 cm. The focal length of the concave mirror is:
Define the term Principal focus.
What is the relationship between the focal length and radius of curvature?
A shopkeeper wanted to fix a mirror that will give a maximum view of his shop. What type of mirror should he use? Give reason.
