Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Complete the following diagrams shown in the below figure by drawing the reflected ray for each incident ray.
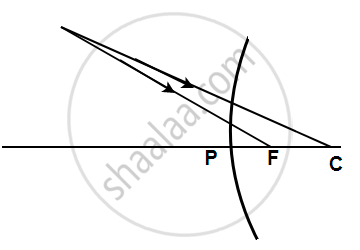
उत्तर
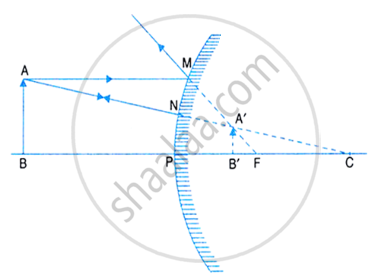
A light ray when produced backwards passes through principal focus as shown in the problem figure. We draw the normal through the centre of curvature at the point of incidence and draw the reflected ray at an angle equal to the angle of incidence thus following the laws of reflection. The reflected ray is parallel to the principal axis. The other ray is passing through the centre of curvature as shown in the problem figure. This ray retraces its incident path because it strikes the mirror normally i.e. 90 degrees. These two reflected rays when produced backwards coincide at a point where the image is formed. The image, A'B' is virtual, erect, and diminished in size.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A simple microscope is used by watch repairers. Give reason.
A student used a device (X) to obtain/focus the image of a well illuminated distant building on a screen (S) as shown below in the diagram. Select the correct statement about the device (X).

Define the following term in the context of spherical mirrors:- Principal axis
Explain the following term related to spherical lenses:- centres of curvature
Match the items given in Column I with one or more items of Column II.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (a) | A plane mirror | (i) | Used as a magnifying glass. |
| (b) | A convex mirror | (ii) | Can form image of objects spread over a large area. |
| (c) | A convex lens | (iii) | Used by dentists to see enlarged image of teeth. |
| (d) | A concave mirror | (iv) | The image is always inverted and magnified. |
| (e) | A concave lens | (v) | The image is erect and of the same size as the object. |
| (vi) | The image is erect and smaller in size than the object. |
Draw separate diagram for the formation of virtual image of an object by a concave mirror.
Name the spherical mirror which (i) diverges (ii) converges the beam of light incident on it. Justify your answer by drawing a ray diagram in each case.
The magnification for a mirror is -3. How are u and v related?
An object forms a virtual image which is 1/8th of the size of the object. If the object is placed at a distance of 40 cm from the convex mirror, calculate:
- the position of the image
- the focal length of the convex mirror.
Define the term Centre of curvature.
