Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
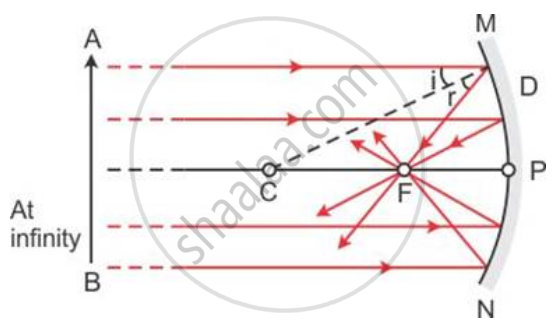
Name the spherical mirror which (i) diverges (ii) converges the beam of light incident on it. Justify your answer by drawing a ray diagram in each case.
उत्तर
(i) Convex mirror diverges a beam of light falling on it.

(ii) Concave mirror converges a beam of light falling on it.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When a spherical mirror is held towards the sun and its sharp image is formed on a piece of a carbon paper for some time, a hole is burnt in the carbon paper.
What is the nature of spherical mirror?
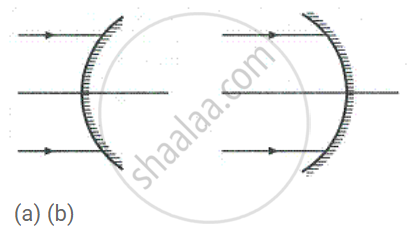
Name the mirrors shown in Figure (a) and (b).
State the two convenient rays that are chosen to construct the image by a spherical mirror for a given object? Explain your answer with the help of suitable ray diagrams.
Discuss the position and nature of image formed by a concave mirror when an object is moved from infinity towards the pole of mirror.
The radius of curvature of a convex mirror is 40 cm. Find its focal length.
Is real image always inverted?
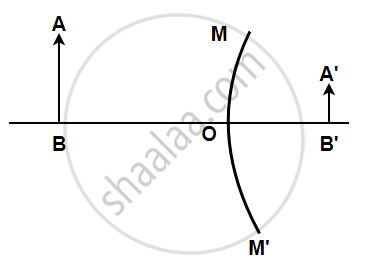
AB is the object, A1B1 is its image. MM' is the position of the mirror. Complete the ray diagram and find the position of the center of curvature and focus of the mirror. Also, measure the focal length.
Define the term Centre of curvature.
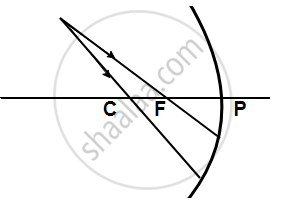
Complete the following diagrams shown in the below figure by drawing the reflected ray for each incident ray.
Define the radius of curvature.
