Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
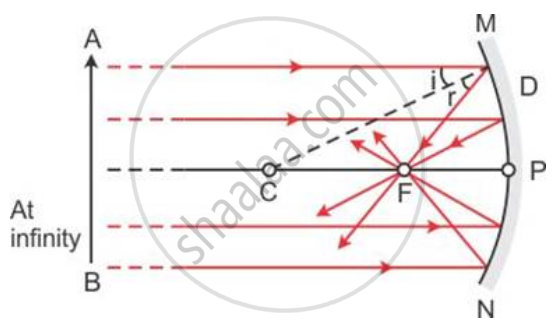
Name the spherical mirror which (i) diverges (ii) converges the beam of light incident on it. Justify your answer by drawing a ray diagram in each case.
उत्तर
(i) Convex mirror diverges a beam of light falling on it.

(ii) Concave mirror converges a beam of light falling on it.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An image that cannot be obtained on a screen is called ______.
What type of image is formed:
on a cinema screen?
Name the spherical mirror which can produce a real and diminished image of an object.
AB and CD, two spherical mirrors, from parts of a hollow spherical ball with its centre at O as shown in the diagram. If arc AB = `1/2` arc CD, what is the ratio of their focal lengths? State which of the two mirrors will always form virtual image of an object placed in front of it and why.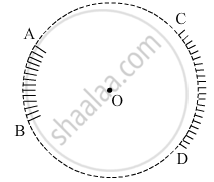
The diagram below in Figure, shows a convex mirror. C is its centre of curvature and F is its focus. (i) Draw two rays from A and hence locate the position of image of object OA. Label the image IB. (ii) State three characteristics of the image.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a concave mirror for an object placed between its pole and focus. State three characteristics of the image.
A concave mirror forms a real image of an object placed in front of it at a distance 30 cm, of size three times the size of object. Find (a) the focal length of mirror (b) position of image.
Define the term Focus of a concave mirror.
Size of image of an object by a mirror having a focal length of 20 cm is observed to be reduced to 1/3rd of its size. At what distance the object has been placed from the mirror? What is the nature of the image and the mirror?
The distance from the center of curvature of the mirror to the pole is called the focal length of the mirror.
