Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Size of image of an object by a mirror having a focal length of 20 cm is observed to be reduced to 1/3rd of its size. At what distance the object has been placed from the mirror? What is the nature of the image and the mirror?
उत्तर
Case I: (In case of convex mirror)
Magnification, `"m" = 1/3` (convex mirror)
Focal length (f) = 20 cm
Size of image `("h"_"i") = 1/3 xx "h"_"o"` (Size of object)
Using the magnification formula,
`"m" = "h"_"i"/"h"_"o" = (-upsilon)/"u"`
Substituting the values in the above equation,
`("h"_"o"/3)/"h"_"o" = (-upsilon)/"u"`
`1/3 = (-upsilon)/"u"`
`upsilon = (-"u")/3`
Using the mirror formula,
`1/upsilon + 1/"u" = 1/"f"`
`(-3)/"u" + 1/"u" = 1/20`
`(-2)/"u" = 1/20`
u = -40 cm
Negative sign shows that the object is in front of the mirror.
Substituting the above value in obtained image distance and object distance relation,
`upsilon = -u/3 = - ((-40))/3 = 40/3` cm
Thus, the image formed is virtual, erect and diminished. The object is at a distance of 40 cm from the mirror.
Case II: In case of concave mirror
Magnification, `"m" = -1/3` (concave mirror)
Focal length (f) = -20 cm
Using the magnification formula,
`"m" = "h"_"i"/"h"_"o" = (-upsilon)/"u"`
Substituting the values in the above equation,
`(-1)/3 = (-upsilon)/"u"`
`1/3 = upsilon/"u"`
`upsilon = "u"/3`
Using the mirror formula,
`1/upsilon + 1/"u" = 1/"f"`
`3/"u" + 1/"u" = 1/(-20)`
`4/"u" = 1/(-20)`
u = -80 cm
`upsilon = "u"/3 = -80/3` cm
Thus, the image will be real and inverted. The object is at a distance of 80 cm from the mirror.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
One half of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm is covered with a black paper. Can such a lens produce an image of a complete object placed at a distance of 30 cm from the lens? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. A 4 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to its principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 15 cm. Find the nature, position and the size of the image.
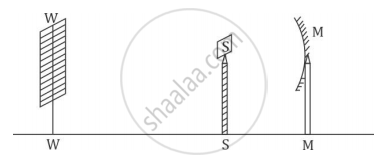
A student obtains a sharp image of the distant window (W) of the school laboratory on the screen (S) using the given concave mirror (M) to determine its focal length. Which of the following distances should he measure to get the focal length of the mirror?
Find out the letters of English alphabet or any other language known to you in which the image formed in a plane mirror appears exactly like the letter itself. Discuss your findings.
Give one use each of a concave and a convex mirror.
Three mirrors are created from a single sphere. Which of the following - pole, centre of curvature, radius of curvature, principal axis - will be common to them and which will not be common?

Draw suitable diagrams to illustrate the action of (i) concave mirror and (ii) convex mirror on a beam of light incident parallel to the principal axis.
