Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
One half of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm is covered with a black paper. Can such a lens produce an image of a complete object placed at a distance of 30 cm from the lens? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. A 4 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to its principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 15 cm. Find the nature, position and the size of the image.
उत्तर
An image is formed from a number of rays from the object getting refracted by the lens. The complete image will be formed even if one half of the lens is covered. However, the brightness of the image will be less.
Case I: When the upper half of the lens is covered
In this case, rays of light coming from the object get refracted by the lower half of the lens. These rays meet at the other side of the lens to form the image of the given object as shown in the following figure:
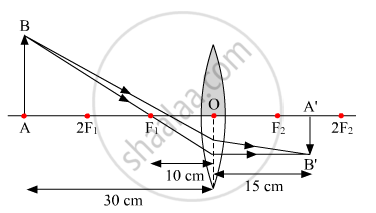
Case II: When the lower half of the lens is covered
A convex lens can produce the complete image of the object even though half of the lens is covered. This is because light coming from the object can be refracted from the other half of the lens. However, the intensity of light will be reduced.

Given:-
Height of the object = h = 4 cm
Focal length of the convex lens = f = 20 cm
Object distance = u = −15 cm
Using the lens formula, we get
`1/`
`therefore1/`
`therefore`
Hence, the image is formed 60 cm in front of the lens on the same side as the object. Because v is negative, we can say that the image is virtual.
From the magnification formula for the lens, we get
`m=(h')/h=`
`thereforeh'=(`
Hence, the size of the image is h′ = 16 cm.
Because the height of the image is positive and greater than the height of the object, the image is erect and magnified.
So, we can conclude that the image is virtual, erect and magnified.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give one use each of a concave and a convex mirror.
Which type of mirror can form a real image?
What happens when a ray of light falls normally (or perpendiculary) on the surface of a plane mirror?
Name the two kinds of spherical mirrors and distinguish between them.
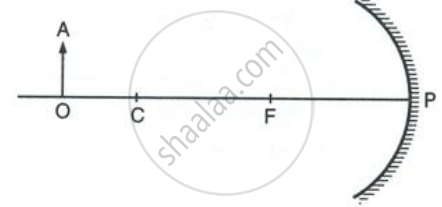
Figure shows a concave mirror with its pole at P, focus F and centre of curvature C. Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object OA.
Discuss the position and nature of image formed by a convex mirror when an object is moved from infinity towards the pole of mirror.
Define the following term in relation to concave mirror.
Pole
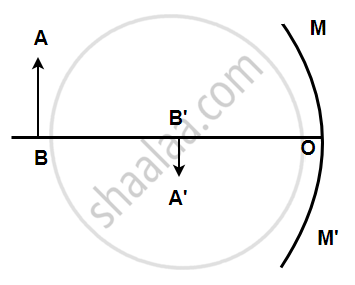
AB is the object, A'B' is the image, and MM' is the position of the mirror. Complete the ray diagram showing the formation of the image and find the focal length of the mirror.
If the focal length of a spherical mirror is 10 cm, what is the value of its radius of curvature?
The distance from the center of curvature of the mirror to the pole is called the focal length of the mirror.
