Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
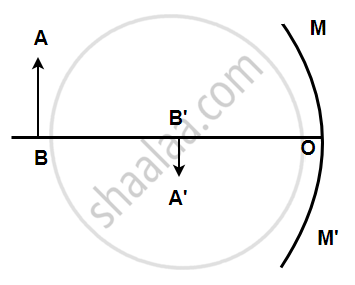
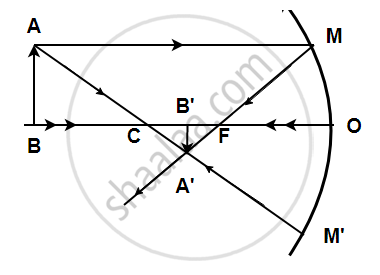
AB is the object, A'B' is the image, and MM' is the position of the mirror. Complete the ray diagram showing the formation of the image and find the focal length of the mirror.
उत्तर
A light ray coming from a point on object AB is reflected from the surface of the mirror, it passes through the principal focus and the other ray passing through the center of curvature strikes the mirror normally i.e. 90 degrees. Hence it will reflect back. These two reflected rays coincide at a point where the image is formed. The image, A'B' is real, inverted, and diminished in size. The focal length was found to be 16 mm.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A 4 cm tall object is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens. The distance of the object from the optical centre of the lens is 12 cm and its sharp image is formed at a distance of 24 cm from it on a screen on the other side of the lens. If the object is now moved a little away from the lens, in which way (towards the lens or away from the lens) will he have to move the screen to get a sharp image of the object on it again? How will the magnification of the image be affected?
A student focused the Sun rays using an optical device 'X' on a screen S as shown.

From this it may be concluded that the device 'X' is a (select the correct option)
(A) Convex lens of focal length 10 cm.
(B) Convex lens of radius of curvature 20 cm.
(C) Convex lens of focal length 20 cm.
(D) Concave mirror of focal length 20 cm.
Explain the following term related to spherical lenses:- principal focus
We can obtain an enlarged and erect image by a convex mirror.
Define (a) centre of curvature (b) radius of curvature (c) pole (d) principal axis, and (e) aperture, of a spherical mirror with the help of a labelled diagram
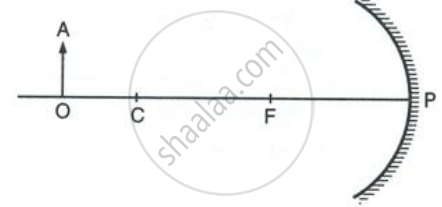
Figure shows a concave mirror with its pole at P, focus F and centre of curvature C. Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object OA.
At what distance from a concave mirror of focal length 25 cm should an object be placed so that the size of image is equal to the size of the object.
Define the term Centre of curvature.
An object 10 cm high is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a spherical mirror of focal length 25 cm. By scale drawing find the nature, position, and magnification of the image in the following case:
Concave mirror
