Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
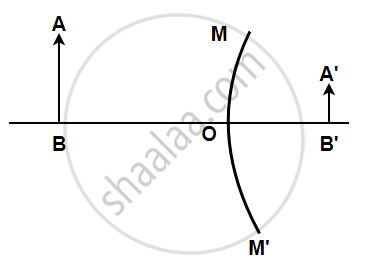
AB is the object, A1B1 is its image. MM' is the position of the mirror. Complete the ray diagram and find the position of the center of curvature and focus of the mirror. Also, measure the focal length.
उत्तर
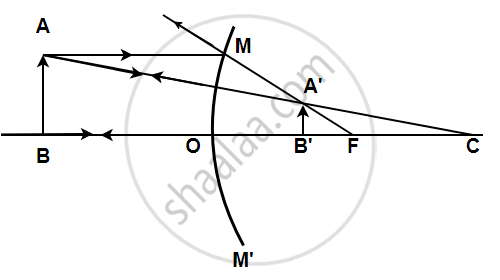
A light ray coming from a point on object AB is reflected from the surface of the mirror. When this ray is produced backwards, it passes through the principal focus and the ray which traces its incident path after reflection, when produced backwards, passes through the centre of curvature. These two reflected rays coincide at a point where the image is formed. The image, A'B' is virtual, erect, and diminished in size The focal length was found to be 24 mm.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define (a) centre of curvature (b) radius of curvature (c) pole (d) principal axis, and (e) aperture, of a spherical mirror with the help of a labelled diagram
When a spherical mirror is held towards the sun and its sharp image is formed on a piece of a carbon paper for some time, a hole is burnt in the carbon paper.
Why is a hole burnt in the carbon paper?
A ray of light travels from a denser medium to a rarer medium. How will it bend?
State the position of object for which the image formed by a concave mirror is of same size.
Does the mirror mentioned in part (b) form real image for all locations of the object?
Name the kind of mirror used to obtain:
A virtual and diminished image
The magnification for a mirror is -3. How are u and v related?
A concave mirror forms a virtual image of size twice that of the object placed at a distance 5 cm from it.
Find : (a) the focal length of the mirror (b) position of image
An object 5 cm high is placed at a distance 60 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. Find the position and size of the image.
An object of height 2 cm is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a concave mirror of a focal length of 12 cm. Find the position, size, and nature of the image.
