Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
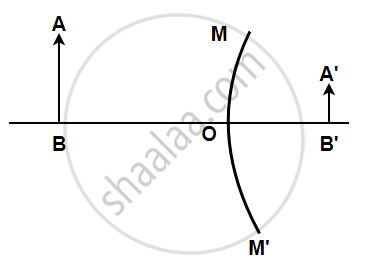
AB is the object, A1B1 is its image. MM' is the position of the mirror. Complete the ray diagram and find the position of the center of curvature and focus of the mirror. Also, measure the focal length.
Solution
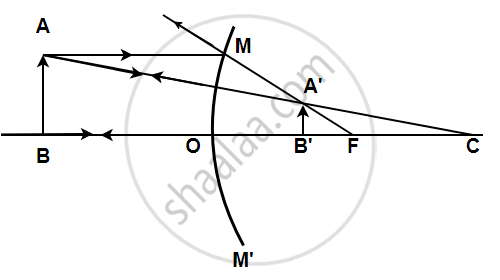
A light ray coming from a point on object AB is reflected from the surface of the mirror. When this ray is produced backwards, it passes through the principal focus and the ray which traces its incident path after reflection, when produced backwards, passes through the centre of curvature. These two reflected rays coincide at a point where the image is formed. The image, A'B' is virtual, erect, and diminished in size The focal length was found to be 24 mm.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
One half of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm is covered with a black paper. Can such a lens produce an image of a complete object placed at a distance of 30 cm from the lens? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. A 4 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to its principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 15 cm. Find the nature, position and the size of the image.
A ray of light strikes a plane mirror at an angle of 40° to the mirror surface. What will be the angle of reflection?
An object of length 4 cm is placed in front of a concave mirror at distance 30 cm. The focal length of mirror is 15 cm.
- Where will the image form?
- What will be the length of image?
An object forms a virtual image which is 1/8th of the size of the object. If the object is placed at a distance of 40 cm from the convex mirror, calculate:
- the position of the image
- the focal length of the convex mirror.
Does the mirror name by your form a real image for all locations? Give a reason for your answer.
Complete the following diagrams shown in the below figure by drawing the reflected ray for each incident ray.
A ray of light is incident towards a plane mirror at an angle of 30° with the mirror surface. What will be the angle of reflection?
