Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An object forms a virtual image which is 1/8th of the size of the object. If the object is placed at a distance of 40 cm from the convex mirror, calculate:
- the position of the image
- the focal length of the convex mirror.
Solution
Let size of the object = h0 = x
Size of the image h1 = `"x"/8` = + 1.25 cm
Distance of the object from the converx mirror = u = - 40 cm
Distance of the image from the convex mirror = v = ?
(i) Magnification = m = `"h"_1/"h"_0 = - "v"/"u"`
`("x"/8)/"x" = - "v"/-40`
v = `"x"/"8x" xx 40 = 5` cm
(ii) Using mirror formula:
`1/"u" + 1/"v" = 1/"f"`
We have,
`1/-40 + 1/5 = 1/"f"`
`1/"f" = - 1/40 + 1/5`
`1/"f" = (- 1 + 8)/40 = 7/40`
⇒ f = `40/7 = 5.71` cm
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
One half of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm is covered with a black paper. Can such a lens produce an image of a complete object placed at a distance of 30 cm from the lens? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. A 4 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to its principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 15 cm. Find the nature, position and the size of the image.
A virtual image larger than the object can be produced by a ______.
Explain the meaning of the terms focus and focal length in case of a convex mirror, with the help of suitable ray diagram.
Name the mirrors shown in Figure (a) and (b).
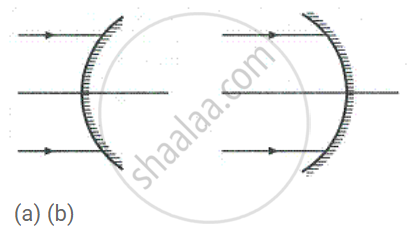
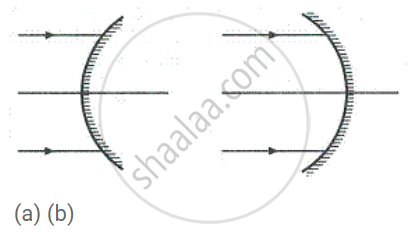
In each case (a) and (b), draw reflected rays for the given incident rays and mark focus by the symbol F.
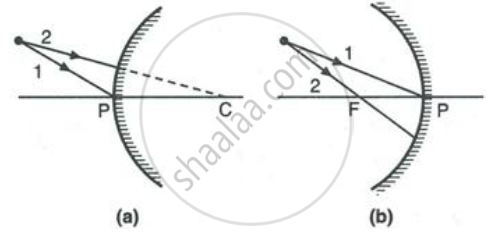
Complete the following diagrams in Figure by drawing the reflected rays for the incident rays 1 and 2.
The diagram below in Figure, shows a convex mirror. C is its centre of curvature and F is its focus. (i) Draw two rays from A and hence locate the position of image of object OA. Label the image IB. (ii) State three characteristics of the image.
Does the mirror mentioned in part (b) form real image for all locations of the object?
Is real image always inverted?
Define linear magnification produced by a mirror?
