Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An object forms a virtual image which is 1/8th of the size of the object. If the object is placed at a distance of 40 cm from the convex mirror, calculate:
- the position of the image
- the focal length of the convex mirror.
उत्तर
Let size of the object = h0 = x
Size of the image h1 = `"x"/8` = + 1.25 cm
Distance of the object from the converx mirror = u = - 40 cm
Distance of the image from the convex mirror = v = ?
(i) Magnification = m = `"h"_1/"h"_0 = - "v"/"u"`
`("x"/8)/"x" = - "v"/-40`
v = `"x"/"8x" xx 40 = 5` cm
(ii) Using mirror formula:
`1/"u" + 1/"v" = 1/"f"`
We have,
`1/-40 + 1/5 = 1/"f"`
`1/"f" = - 1/40 + 1/5`
`1/"f" = (- 1 + 8)/40 = 7/40`
⇒ f = `40/7 = 5.71` cm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A simple microscope is used by watch repairers. Give reason.
We can obtain a real, enlarged and inverted image by a concave mirror.
A ray of light is incident normally on a plane mirror. What will be the
angle of incidence?
Three mirrors are created from a single sphere. Which of the following - pole, centre of curvature, radius of curvature, principal axis - will be common to them and which will not be common?

Define the terms pole, principal axis and centre of curvature with reference to a spherical mirror.
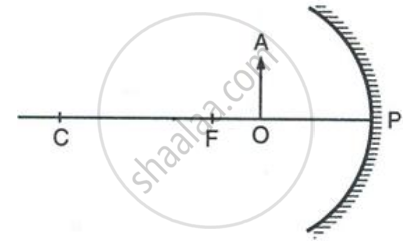
Figure shows a concave mirror with its pole at P, focus F and centre of curvature C. Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object OA.
What is meant by magnification? Write its expression. What is its sign for the (a) real (b) virtual, image?
Define the term Pole.
AB is the object, A1B1 is its image. MM' is the position of the mirror. Complete the ray diagram and find the position of the center of curvature and focus of the mirror. Also, measure the focal length.