Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A simple microscope is used by watch repairers. Give reason.
उत्तर
When an object is placed within the focal length of a simple microscope, its magnified and erect image is obtained on the same side of the lens as that of the object. So, a watch repairer sees the minute parts of a watch very clearly with a simple microscope by adjusting the distance between the object and the lens. This helps in repairing the watch. Hence, a simple microscope is used by watch repairers.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
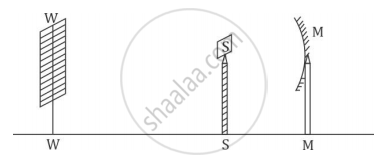
A student obtains a sharp image of the distant window (W) of the school laboratory on the screen (S) using the given concave mirror (M) to determine its focal length. Which of the following distances should he measure to get the focal length of the mirror?
A student used a device (X) to obtain/focus the image of a well illuminated distant building on a screen (S) as shown below in the diagram. Select the correct statement about the device (X).

An image that cannot be obtained on a screen is called ______.
What is the relation between the focal length and radius of curvature of a spherical mirror (concave mirror of convex mirror)? Calculate the focal length of a spherical mirror whose radius of curvature is 25 cm.
Complete the following sentence:
All the distances are measured from the .......... of a spherical mirror.
Name the spherical mirror which can produce a virtual and diminished image of an object.
The diverging lens in part (a) is replaced by a converging lens also of focal length 100 mm. The object remains in the same position and an image is formed by the converging lens. Compare two properties of this image with those of the image formed by the diverging lens in part (a).
A coin placed at the bottom of a vessel appears to be raised when water is poured in the vessel.
Explain the following terms :
Pole, Centre of curvature, Radius of curvature, Principal axis. Show them on separate diagrams for each of the concave and convex mirrors.
An optical device has been given to a student and he determines its focal length by focusing the image of the sun on a screen placed 24 cm from the device on the same side as the sun. Select the correct statement about the device.
(A) Convex mirror of focal length 12 cm
(B) Convex lens of focal length 24 cm
(C) Concave mirror of focal length 24 cm
(D) Convex lens of focal length 12 cm
A student obtained on a screen the sharp image of a candle flame placed at the farther end of laboratory table using a concave mirror. For getting better value of focal length of the mirror, the teacher suggested to him to focus the sun. What should the student do?
(A) Should move the mirror away from the screen.
(B) Should move the mirror towards the screen.
(C) Should move the mirror and screen both towards the sun.
(D) Should move only the screen towards the sun.
Explain the meaning of the terms focus and focal length in case of a convex mirror, with the help of suitable ray diagram.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a concave mirror for an object placed between its pole and focus. State three characteristics of the image.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a concave mirror for the object beyond its centre of curvature. State three characteristics of the image.
Does the mirror mentioned in part (b) form real image for all locations of the object?
Name the kind of mirror used to obtain:
A virtual and enlarged image
For an incident ray directed towards centre of curvature of a spherical mirror the reflected ray:
The radius of curvature of a convex mirror is 40 cm. Find its focal length.
A point light source is kept in front of a convex mirror at a distance of 40 cm. The focal length of the mirror is 40 cm. Find the position of image.
An object 5 cm high forms a virtual image of 1.25 cm high, when placed in front of a convex mirror at a distance of 24 cm. Calculate:
- the position of the image
- the focal length of the convex mirror.
Select the correct option:
Looking into a mirror one finds her image diminished, the mirror is:
Define the following term:
spherical mirror
Define the following term in relation to concave mirror.
Aperture
Define the term Centre of curvature.
Define linear magnification produced by a mirror?
Define the term Pole.
Define the term Normal.
Define the term Principle focus.
Draw a ray diagram to show that a convex mirror has a wider field of view.
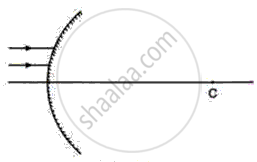
The diagram below shows the parallel rays incident on a convex mirror. C is the centre of the curvature of the mirror. By drawing the paths of the reflected rays, label the focus F and hence find the focal length of the mirror.
The spherical mirror used as a rear view mirror in the vehicle is
If the real image of a candle flame formed by a lens is three times the size of the flame and the distance between lens and image is 80 cm, at what distance should the candle be placed from the lens?
A shopkeeper wanted to fix a mirror that will give a maximum view of his shop. What type of mirror should he use? Give reason.
How tall does a mirror have to be to fit an entire person’s body?
