Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Three mirrors are created from a single sphere. Which of the following - pole, centre of curvature, radius of curvature, principal axis - will be common to them and which will not be common?

उत्तर
Let us name the mirrors M1, M2 and M3 as shown below.
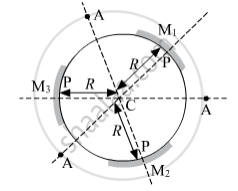
From the figure, we see that
- pole (P) is not common.
- centre of curvature (C) is common.
- principal axis (PA) is not common.
- radius of curvature (R) is common. The radius of curvature is the radius of the sphere. In the given figure, the length CP is the same for all mirrors.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the following term related to spherical lenses:- principal focus
Name the spherical mirror which can produce a virtual and diminished image of an object.
The shiny outer surface of a hollow sphere of aluminium of radius 50 cm is to be used as a mirror:
State whether this spherical mirror will diverge or converge light rays.
AB and CD, two spherical mirrors, from parts of a hollow spherical ball with its centre at O as shown in the diagram. If arc AB = `1/2` arc CD, what is the ratio of their focal lengths? State which of the two mirrors will always form virtual image of an object placed in front of it and why.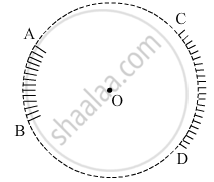
Draw suitable diagrams to illustrate the action of (i) concave mirror and (ii) convex mirror on a beam of light incident parallel to the principal axis.
Explain the meaning of the terms focus and focal length in case of a convex mirror, with the help of suitable ray diagram.
Complete the following diagrams in Figure by drawing the reflected rays for the incident rays 1 and 2.
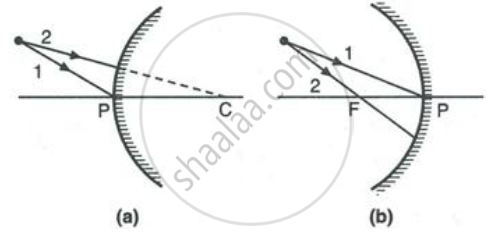
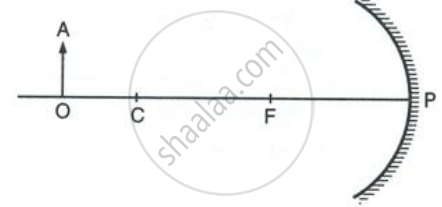
Figure shows a concave mirror with its pole at P, focus F and centre of curvature C. Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object OA.
Name the mirror which always produces an erect and virtual image. How is the size of image related to the size of object?
Upto what maximum distance from a concave mirror, the image can be obtained? What will be the location of object for it?
For an incident ray directed towards centre of curvature of a spherical mirror the reflected ray:
When an object of height 1 cm is kept at a distance 4 cm from a concave mirror, its erect image of height 1.5 cm is formed at a distance 6 cm behind the mirror. Find the focal length of mirror, by drawing.
A straight stick partly dipped in water obliquely, appears to be bent at the surface of water.
What is a mirror formula?
Define linear magnification produced by a mirror?
In torches, search lights and headlights of vehicles the bulb is placed ______.
Spherical mirrors are one form of ______ mirrors.
Explain why a ray of light passing through the center of curvature of a concave mirror, gets reflected along with the same pattern.
