Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Three mirrors are created from a single sphere. Which of the following - pole, centre of curvature, radius of curvature, principal axis - will be common to them and which will not be common?

Solution
Let us name the mirrors M1, M2 and M3 as shown below.
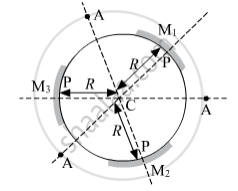
From the figure, we see that
- pole (P) is not common.
- centre of curvature (C) is common.
- principal axis (PA) is not common.
- radius of curvature (R) is common. The radius of curvature is the radius of the sphere. In the given figure, the length CP is the same for all mirrors.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A simple microscope is used by watch repairers. Give reason.
Explain the following term related to spherical lenses:- centres of curvature
Explain the following term related to spherical lenses:- principal focus
An image which can be obtained on a screen is called a ______ image.
When a spherical mirror is held towards the sun and its sharp image is formed on a piece of a carbon paper for some time, a hole is burnt in the carbon paper.
At which point of the spherical mirror the carbon paper is placed?
Name the spherical mirror which can produce a real and diminished image of an object.
What do you understand by the focus and focal length of a spherical mirror? Show them on the separate diagrams for each of a concave mirror and a convex mirror.
A student obtained on a screen the sharp image of a candle flame placed at the farther end of laboratory table using a concave mirror. For getting better value of focal length of the mirror, the teacher suggested to him to focus the sun. What should the student do?
(A) Should move the mirror away from the screen.
(B) Should move the mirror towards the screen.
(C) Should move the mirror and screen both towards the sun.
(D) Should move only the screen towards the sun.
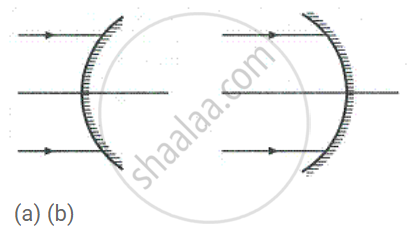
Name the mirrors shown in Figure (a) and (b).
The radius of curvature of a convex mirror is 40 cm. Find its focal length.
The image formed by a convex mirror is of size one third the size of object. How are u and v related?
An object 10 cm high is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a spherical mirror of focal length 25 cm. By scale drawing find the nature, position, and magnification of the image in the following case:
Convex mirror
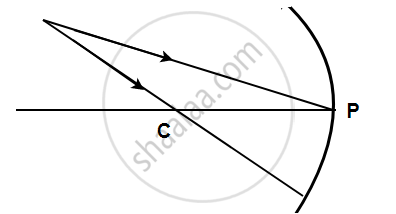
The following Figure shows a concave mirror MM' on which a ray of light incident from a point P gets reflected to meet the principle axis at O.
(a) Find, by construction, the position of the centre of curvature of the concave mirror.
(b) Write down the value for the radius of curvature of the mirror.
(c) Calculate the focal length of the mirror.
(d ) Which relation is used in deducing the focal length from the radius of curvature?
Complete the following diagrams shown in the following figures by drawing the reflected rays.
The image formed in a plane mirror is always inverted.
What is the focal length (f) of a mirror?
Define the radius of curvature.
