Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
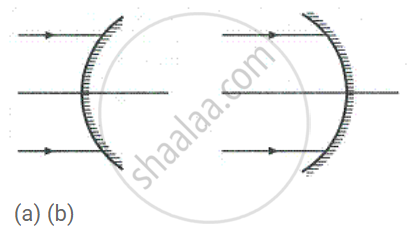
Name the mirrors shown in Figure (a) and (b).
Solution
(i) In figure (a) a convex mirror is shown.
In figure (b) a concave mirror is shown.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name the two types of spherical mirrors. What type of mirror is represented by the:
back side of a shining steel spoon?
Define (a) centre of curvature (b) radius of curvature (c) pole (d) principal axis, and (e) aperture, of a spherical mirror with the help of a labelled diagram
A lens forms a real image 3 cm high of an object 1 cm high. If the separation of object and image is 15 cm, find the focal length of the lens.
State the two kinds of spherical mirror and distinguish them with the aid of proper diagrams.
Three mirrors are created from a single sphere. Which of the following - pole, centre of curvature, radius of curvature, principal axis - will be common to them and which will not be common?

Discuss the position and nature of image formed by a concave mirror when an object is moved from infinity towards the pole of mirror.
How is the focal length of a spherical mirror related to its radius of curvature?
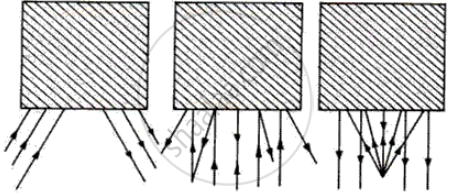
The boxes in figure (a, b, c) represent mirrors; insert a mirror which will reflect the incident ray as shown in the diagram.
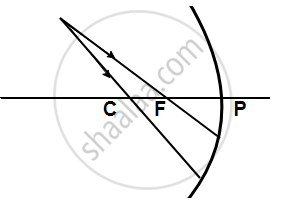
AB is the object, A1B1 is its image. MM' is the position of the mirror. Complete the ray diagram and find the position of the center of curvature and focus of the mirror. Also, measure the focal length.
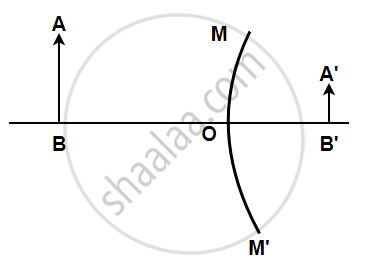
Complete the following diagrams shown in the below figure by drawing the reflected ray for each incident ray.