Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
![Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 7 - Reflection of Light Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 7 - Reflection of Light - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-physics-english-class-9-icse_6:8a0c4572dea049a29e575abe2d9ca662.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 7: Reflection of Light
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 7 of CISCE Selina for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 7 Reflection of Light Exercise 7 (A) [Pages 153 - 154]
What do you mean by reflection of light?
State which surface of a plane mirror reflects most of the light incident on it: the front smooth surface or the back silvered surface.
Explain the following term :
Plane mirror
Draw diagram/diagrams to show them.
Explain the following term:
Incident ray
Draw diagram/diagrams to show them.
Explain the following term:
Reflected ray
Draw diagram/diagrams to show them.
Explain the following term:
Angle of incidence
Draw diagram/diagrams to show them.
Explain the following term:
Angle of reflection.
Draw diagram/diagrams to show them.
With the help of diagrams, explain the difference between the regular and irregular reflection.
Differentiate between the reflection of light from a plane mirror and that from a plane sheet of paper.
State the two laws of reflection of light.
State the laws of reflection and describe an experiment to verify them.
A light ray is incident normally on a plane mirror. (a) What is its angle of incidence?
A light ray is incident normally on a plane mirror. What is the direction of reflected ray? Show it on a diagram.
Draw a diagram to show the reflection of a ray of light using a plane mirror. In the diagram, label the incident ray, the reflected ray, the normal, the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection.
Figure shows an incident ray AO and the normal ON on a plane mirror. The angle which the incident ray AO makes with mirror is 30°. (a) Find the angle of incidence. (b) Draw the reflected ray and then find the angle between the incident and reflected rays.

The diagram in Figure shows a point object P in front of a plane mirror MM1.

(a) Complete the diagram by taking two rays from the point P to show the formation of its image.
(b) In the diagram, mark the position of eye to see the image.
(c) Is the image formed real or virtual? Explain why?
The diagram below in figure shows an object XY in front of a plane mirror MM1 . Draw on the diagram, path of two rays from each point X and Y of the object to show the formation of its image .

Write three characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror?
How is the position of an image related to the position of the object?
Differentiate between a real and a virtual image.
What is meant by lateral inversion of an image in a plane mirror? Explain it with the help of a ray diagram.
The letters on the front of an ambulance are written laterally inverted like 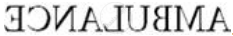 . Give reason.
. Give reason.
Why is it difficult to read the image of the text of a page formed due to reflection by a plane mirror?
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 7 Reflection of Light Exercise 7 (A) [Page 154]
According to the law of reflection :
i/r = constant
sin i /sin r = constant
i + r = constant
i = r
The image formed by a plane mirror is :
Erect and diminished
Erect and enlarged
Inverted and of same size
Erect and of same size
The image formed by a plane mirror is :
real
virtual
virtual with lateral inversion
real with lateral inversion
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 7 Reflection of Light Exercise 7 (A) [Page 154]
A ray is incident on a plane mirror . Its reflected ray is perpandicular to the incident ray . Find the angle of incidence .
A man standing in front of a plane mirror finds his image at a distance 6 metre from himself. What is the distance of man from the mirror?
An insect is sitting in front of a plane mirror at a distance 1 m from it.
(a) Where is the image of the insect formed?
An insect is sitting in front of a plane mirror at a distance 1 m from it.
(b) What is the distance between the insect and its image?
An object is kept at 60 cm in front of a plane mirror. If the mirror is now moved 25 cm away from the object, how does the image shift from its previous position?
An optician while testing the eyes of a patient keeps a chart of letters 3 m behind the patient and asks him to see the letters on the image of chart formed in a plane mirror kept at distance 2 m in front of him. At what distance is the chart seen by the patient?
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 7 Reflection of Light Exercise 7 (B) [Page 157]
Two plane mirrors are placed making an angle θ in between them. Write an expression for the number of images formed of an object placed in between the mirrors. State the condition, if any.
Two plane mirrors are placed making an angle θ° in between them. For an object placed in between the mirrors, if angle is gradually increased from 0° to 180°, how will the number of images change : increase, decrease or remain unchanged?
How many images are formed for a point object kept in between two plane mirrors at right angles to each other? Show them by drawing a ray diagram.
Two plane mirrors are arranged parallel and facing each other at some separation. How many images are formed for a point object kept in between them? Show the formation of images with the help of a ray diagram
State two uses of a plane mirror.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 7 Reflection of Light Exercise 7 (B) [Page 157]
Two plane mirrors are placed making an angle 60° in between them. For an object placed in between the mirrors, the number of images formed will be :
3
6
5
infinite
In the barber's shop, two plane mirrors are placed :
Perpendicular to each other
Parallel to each other
At an angle 60° between them
At angle 45° between them
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 7 Reflection of Light Exercise 7 (B) [Page 157]
State the number of images of an object placed between two mirrors, formed in each case when mirrors are inclined to each other at (a) 90°, and (b) 60°.
An object is placed (i) asymmetrically (ii) symmetrically, between two plane mirrors inclined at an angle of 50°. Find the number of images formed.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 7 Reflection of Light Exercise 7 (C) [Pages 170 - 172]
What is a spherical mirror?
Name the two kinds of spherical mirrors and distinguish between them.
Define the terms pole, principal axis and centre of curvature with reference to a spherical mirror.
Draw suitable diagrams to illustrate the action of (i) concave mirror and (ii) convex mirror on a beam of light incident parallel to the principal axis.
Name the spherical mirror which (i) diverges (ii) converges the beam of light incident on it. Justify your answer by drawing a ray diagram in each case.
Define the terms focus and focal length of a concave mirror. Draw diagram to illustrate your answer.
Explain the meaning of the terms focus and focal length in case of a convex mirror, with the help of suitable ray diagram.
State the direction of incident ray which after reflection from a spherical mirror retraces its path. Give a reason to your answer.
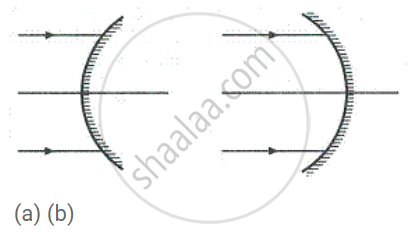
Name the mirrors shown in Figure (a) and (b).
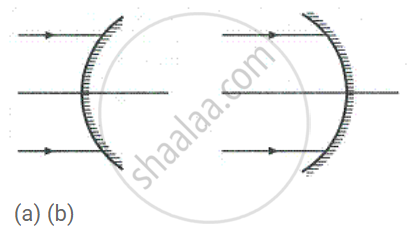
In each case (a) and (b), draw reflected rays for the given incident rays and mark focus by the symbol F.
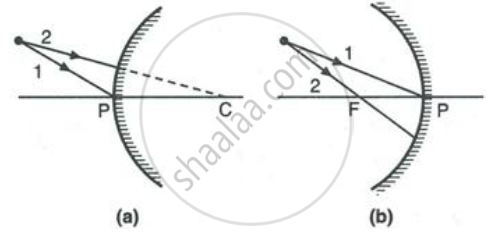
Complete the following diagrams in Figure by drawing the reflected rays for the incident rays 1 and 2.
Complete the following diagrams shown in Fig. by drawing the reflected ray for each of the incident ray A and B.
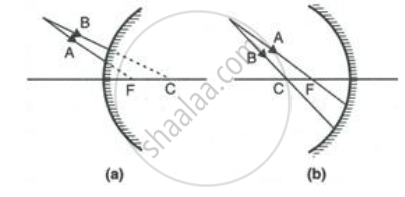
State the two convenient rays that are chosen to construct the image by a spherical mirror for a given object? Explain your answer with the help of suitable ray diagrams.
Figure shows a concave mirror with its pole at P, focus F and centre of curvature C. Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object OA.
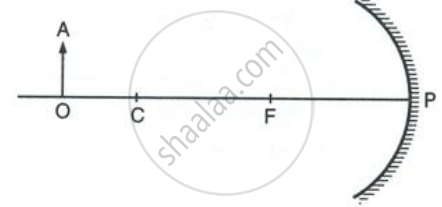
Figure shows a concave mirror with its pole at P, focus F and centre of curvature C. Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object OA.
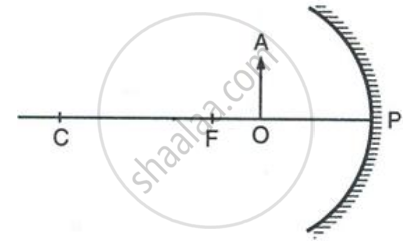
The diagram below in Figure, shows a convex mirror. C is its centre of curvature and F is its focus. (i) Draw two rays from A and hence locate the position of image of object OA. Label the image IB. (ii) State three characteristics of the image.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a concave mirror for an object placed between its pole and focus. State three characteristics of the image.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a concave mirror for the object beyond its centre of curvature. State three characteristics of the image.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object kept in front of a convex mirror. State three characteristics of the image.
Name the mirror which always produces an erect and virtual image. How is the size of image related to the size of object?
For what position of object, the image formed by a concave mirror is magnified and erect?
State whether the image in part (a) is real or virtual?
State the position of object for which the image formed by a concave mirror is of same size.
Write two more characteristics of the image.
What is a real image?
What type of mirror can be used to obtain a real image of an object?
Does the mirror mentioned in part (b) form real image for all locations of the object?
Discuss the position and nature of image formed by a concave mirror when an object is moved from infinity towards the pole of mirror.
Discuss the position and nature of image formed by a convex mirror when an object is moved from infinity towards the pole of mirror.
Name the kind of mirror used to obtain :
A real and enlarged image
Name the kind of mirror used to obtain:
A virtual and enlarged image
Name the kind of mirror used to obtain:
A virtual and diminished image
Name the kind of mirror used to obtain:
A real and diminished image.
How is the focal length of a spherical mirror related to its radius of curvature?
Write the spherical mirror's formula and explain the meaning of each symbol used in it.
What is meant by magnification? Write its expression. What is its sign for the (a) real (b) virtual, image?
Upto what maximum distance from the pole the image in a convex mirror can be obtained? what will be the location of object then ?
Upto what maximum distance from a concave mirror, the image can be obtained? What will be the location of object for it?
How will you distinguish between a plane mirror, a concave mirror and a convex mirror, without touching them?
State two uses of a concave mirror.
State the kind of mirror used
(a) By a dentist,
(b) As a search-light reflector.
(a) When a concave mirror is used as a shaving mirror, where is the person's face in relation to the focus of mirror?
(b) State three characteristics of the image seen in part (a).
Which mirror will you prefer to use as a rear view mirror in a car : plane mirror or convex mirror? Give one reason.
Why does a driver use a convex mirror instead of a plane mirror as a rear view mirror?
Illustrate your answer with the help of a ray diagram.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 7 Reflection of Light Exercise 7 (C) [Page 172]
For an incident ray directed towards centre of curvature of a spherical mirror the reflected ray:
Retraces its path
Passes through the focus
Passes through the pole
Becomes parallel to the principal axis.
The image formed by a convex mirror is
Erect and diminished.
Erect and enlarged.
Inverted and diminished.
Inverted and enlarged.
A real and enlarged image can be obtained by using a
Convex mirror
Plane mirror
Concave mirror
Either convex or plane mirror.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 7 Reflection of Light Exercise 7 (C) [Page 172]
The radius of curvature of a convex mirror is 40 cm. Find its focal length.
The focal length of a concave mirror is 10 cm. Find its radius of curvature.
An object of height 2 cm is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a concave mirror of a focal length of 12 cm. Find the position, size, and nature of the image.
An object is placed at 4 cm distance in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 24 cm. Find the position of image. Is the image magnified?
At what distance from a concave mirror of focal length 25 cm should an object be placed so that the size of image is equal to the size of the object.
An object 5 cm high is placed at a distance 60 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. Find the position and size of the image.
A point light source is kept in front of a convex mirror at a distance of 40 cm. The focal length of the mirror is 40 cm. Find the position of image.
When an object of height 1 cm is kept at a distance 4 cm from a concave mirror, its erect image of height 1.5 cm is formed at a distance 6 cm behind the mirror. Find the focal length of mirror, by drawing.
An object of length 4 cm is placed in front of a concave mirror at distance 30 cm. The focal length of mirror is 15 cm.
- Where will the image form?
- What will be the length of image?
A concave mirror forms a real image of an object placed in front of it at a distance 30 cm, of size three times the size of object. Find (a) the focal length of mirror (b) position of image.
A concave mirror forms a virtual image of size twice that of the object placed at a distance 5 cm from it.
Find : (a) the focal length of the mirror (b) position of image
The image formed by a convex mirror is of size one third the size of object. How are u and v related?
The erect image formed by a concave mirror is of size double the size of object. How are u and v related?
The magnification for a mirror is -3. How are u and v related?
Solutions for 7: Reflection of Light
![Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 7 - Reflection of Light Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 7 - Reflection of Light - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-physics-english-class-9-icse_6:8a0c4572dea049a29e575abe2d9ca662.jpg)
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 7 - Reflection of Light
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE 7 (Reflection of Light) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 7 Reflection of Light are Rules for the Construction of Image Formed by a Spherical Mirror, Focus and Focal Length, Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors, Concave Mirror, Image Formation by Concave Mirror, Convex Mirror, Mirror Equation/Formula, Images Formed by a Plane Mirrors, Distinction Between a Plane Mirror, Concave Mirror and Convex Mirror, Images Formed in a Pair of Mirrors Placed Parallel to Each Other, Images Formed by Two Mirrors Placed Perpendicular to Each Other, Spherical Mirrors, Image Formation by Convex Mirror, Relationship Between the Focal Length and Radius of Curvature, Sign Convention, Reflection of Light, Types of Reflection, Terms Used in Reflection of Light, Law of Reflection of Light, Verification of the Law of Reflection of Light, Formation of Image by Reflection: Real and Virtual Image, Formation of Image of a Point Object by a Plane Mirror, Image of an Extended Object Formed by a Plane Mirror, Position of Image, Lateral Inversion, Plane Mirror, Images Formed in Two Inclined Mirrors.
Using Selina Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE solutions Reflection of Light exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 7, Reflection of Light Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
