Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object kept in front of a convex mirror. State three characteristics of the image.
Solution

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain the following term related to spherical lenses:- centres of curvature
Match the items given in Column I with one or more items of Column II.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (a) | A plane mirror | (i) | Used as a magnifying glass. |
| (b) | A convex mirror | (ii) | Can form image of objects spread over a large area. |
| (c) | A convex lens | (iii) | Used by dentists to see enlarged image of teeth. |
| (d) | A concave mirror | (iv) | The image is always inverted and magnified. |
| (e) | A concave lens | (v) | The image is erect and of the same size as the object. |
| (vi) | The image is erect and smaller in size than the object. |
What is a spherical mirror?
Complete the following diagrams shown in Fig. by drawing the reflected ray for each of the incident ray A and B.
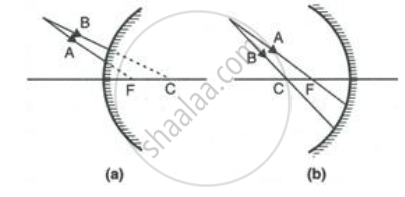
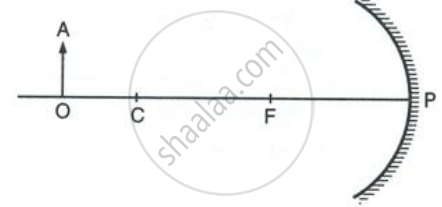
Figure shows a concave mirror with its pole at P, focus F and centre of curvature C. Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object OA.
Define the term principal focus in case of convex mirror. Draw a convex mirror and show its principal focus and focal length clearly.
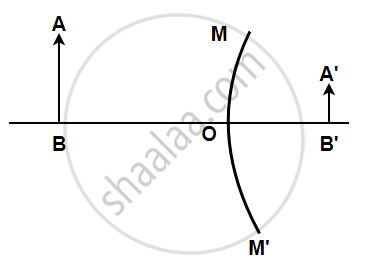
AB is the object, A1B1 is its image. MM' is the position of the mirror. Complete the ray diagram and find the position of the center of curvature and focus of the mirror. Also, measure the focal length.
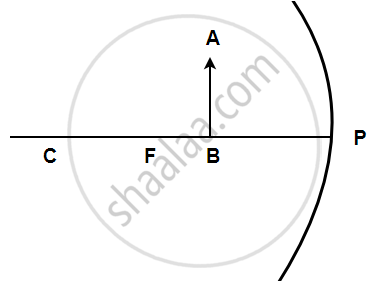
In the following figure shows a concave mirror with its pole (P), focus (F) and centre of curvature (C). Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image of an object AB by the concave mirror.
Define focal length.
