Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The diagram below in Figure, shows a convex mirror. C is its centre of curvature and F is its focus. (i) Draw two rays from A and hence locate the position of image of object OA. Label the image IB. (ii) State three characteristics of the image.
Solution
The ray diagram shows two light rays from A.
The image of the object OA is formed between the focus and the pole on the other side of the mirror.

The image so formed is erect, virtual and diminished.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain the following term related to spherical lenses:- optical centre
A lens forms a real image 3 cm high of an object 1 cm high. If the separation of object and image is 15 cm, find the focal length of the lens.
Explain the meaning of the terms focus and focal length in case of a convex mirror, with the help of suitable ray diagram.
Name the mirrors shown in Figure (a) and (b).
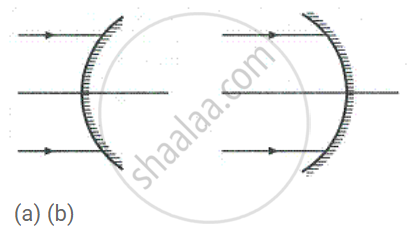
State two uses of a concave mirror.
How will you distinguish between a plane mirror, a concave mirror and a convex mirror, without touching them?
The following Figure shows a concave mirror MM' on which a ray of light incident from a point P gets reflected to meet the principle axis at O.
(a) Find, by construction, the position of the centre of curvature of the concave mirror.
(b) Write down the value for the radius of curvature of the mirror.
(c) Calculate the focal length of the mirror.
(d ) Which relation is used in deducing the focal length from the radius of curvature?
Numerical problem.
The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 25 cm. Find its focal length.
Define the radius of curvature.
