Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
State two uses of a concave mirror.
Give the uses of a concave mirror.
Solution 1
Two uses of concave mirror:
(i) It is used as a shaving mirror.
(ii) It is used as reflector in torch, head light of automobiles etc.
Solution 2
The uses of a concave mirror are
(i) In torches and headlights: The source of light is placed at the focus to obtain a parallel beam of light.
(ii) In floodlights: The source of light is placed just beyond the center of curvature so as to get an intense beam of light.
(iii) Reflecting mirrors for projector lamps: The object is placed at the center of curvature to obtain an image of the same size.
- To collect heat radiations in solar devices: Heat radiations from the sum coming from infinity are brought to focus by a concave mirror in its focal plane.
- Shaving mirror, dentist’s mirror: It produces an erect virtual and highly magnified image of an object placed between its pole and focus.
vi. Solar furnaces: Large concave mirrors are used to concentrate sunlight to produce heat in a solar furnace.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An image formed by a ______ mirror is always of the same size as that of the object.
An image which can be obtained on a screen is called a ______ image.
We can obtain a real, enlarged and inverted image by a concave mirror.
A ray of light is incident normally on a plane mirror. What will be the
angle of incidence?
Complete the following sentence:
All the distances are measured from the .......... of a spherical mirror.
State the two kinds of spherical mirror and distinguish them with the aid of proper diagrams.
State the direction of incident ray which after reflection from a spherical mirror gets reflected along its own path. Give a reason.
Three mirrors are created from a single sphere. Which of the following - pole, centre of curvature, radius of curvature, principal axis - will be common to them and which will not be common?

State the number of images of an object placed between two mirrors, formed in each case when mirrors are inclined to each other at (a) 90°, and (b) 60°.
Explain the meaning of the terms focus and focal length in case of a convex mirror, with the help of suitable ray diagram.
Complete the following diagrams in Figure by drawing the reflected rays for the incident rays 1 and 2.
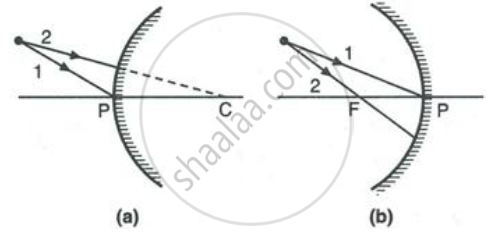
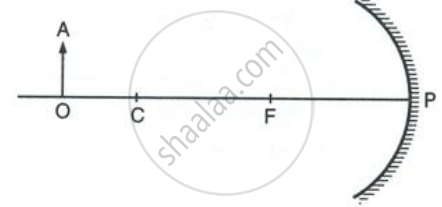
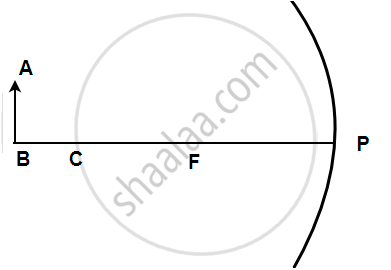
Figure shows a concave mirror with its pole at P, focus F and centre of curvature C. Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object OA.
Which mirror will you prefer to use as a rear view mirror in a car : plane mirror or convex mirror? Give one reason.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object kept in front of a convex mirror. State three characteristics of the image.
The radius of curvature of a convex mirror is 40 cm. Find its focal length.
The erect image formed by a concave mirror is of size double the size of object. How are u and v related?
A concave mirror forms a real image of an object placed in front of it at a distance 30 cm, of size three times the size of object. Find (a) the focal length of mirror (b) position of image.
When an object of height 1 cm is kept at a distance 4 cm from a concave mirror, its erect image of height 1.5 cm is formed at a distance 6 cm behind the mirror. Find the focal length of mirror, by drawing.
A point light source is kept in front of a convex mirror at a distance of 40 cm. The focal length of the mirror is 40 cm. Find the position of image.
An object 5 cm high is placed at a distance 60 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. Find the position and size of the image.
The sun is seen before the sunrise and after the sunset.
Draw a ray diagram in each of the following cases to show the formation of image, when the object is placed :
(i) between the optical centre and principal focus of a convex lens.
(ii) anywhere in front of a concave lens.
(iii) at 2F of a convex lens.
State the signs and values of magnifications in the above-mentioned cases (i) and (ii).
Answer the following question.
Write the modification in the curvature of the eye lens which enables us to see the nearby objects clearly?
Select the correct option:
A mirror forms a virtual image (diminished) of an object, whatever be the position of object:
Select the correct option:
Looking into a mirror one finds her image diminished, the mirror is:
Define the following term in relation to concave mirror.
Center of curvature
Define the following term in relation to concave mirror.
Principal focus
Is real image always inverted?
Define the term Aperture.
Define linear magnification produced by a mirror?
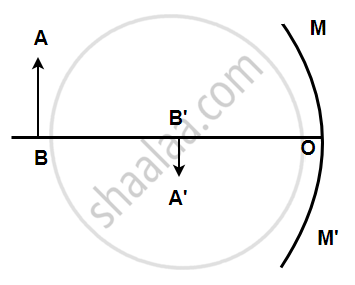
AB is the object, A'B' is the image, and MM' is the position of the mirror. Complete the ray diagram showing the formation of the image and find the focal length of the mirror.
In the following figure shows a concave mirror with its pole (P), focus (F) and centre of curvature (C). Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image of an object AB by the concave mirror.
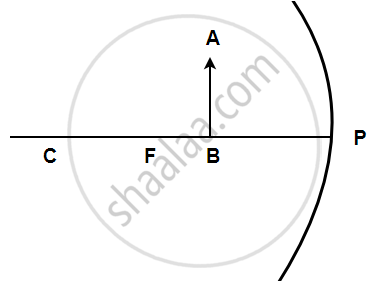
The following figure shows a concave mirror with its pole (P), focus (F), and center of curvature (C). Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image of an object AB by the concave mirror.
A concave mirror can be used to produce a parallel beam of light. Draw a ray to illustrate this.
An object 10 cm high is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a spherical mirror of focal length 25 cm. By scale drawing find the nature, position, and magnification of the image in the following case:
Concave mirror
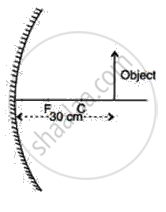
An object is placed in front of a concave mirror as shown in the following figure. By scale drawing, find the nature of the image. Given f = 10 cm, v = 30 cm.
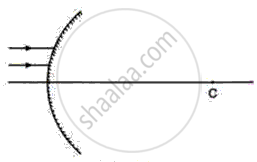
The diagram below shows the parallel rays incident on a convex mirror. C is the centre of the curvature of the mirror. By drawing the paths of the reflected rays, label the focus F and hence find the focal length of the mirror.
In torches, search lights and headlights of vehicles the bulb is placed ______.
Name the type of mirror used in the following situation:
Solar furnace
Support your answer with reason.
Name the two types of spherical mirrors.
Explain why a ray of light passing through the center of curvature of a concave mirror, gets reflected along with the same pattern.
Visit a nearby hospital. You can also visit the clinic of an ENT specialist, or a dentist. Request the doctor to show you the mirrors used for examining ear, nose, throat and teeth. Can you recognise the kind of mirror used in these instruments?
