Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State two uses of a concave mirror.
Give the uses of a concave mirror.
उत्तर १
Two uses of concave mirror:
(i) It is used as a shaving mirror.
(ii) It is used as reflector in torch, head light of automobiles etc.
उत्तर २
The uses of a concave mirror are
(i) In torches and headlights: The source of light is placed at the focus to obtain a parallel beam of light.
(ii) In floodlights: The source of light is placed just beyond the center of curvature so as to get an intense beam of light.
(iii) Reflecting mirrors for projector lamps: The object is placed at the center of curvature to obtain an image of the same size.
- To collect heat radiations in solar devices: Heat radiations from the sum coming from infinity are brought to focus by a concave mirror in its focal plane.
- Shaving mirror, dentist’s mirror: It produces an erect virtual and highly magnified image of an object placed between its pole and focus.
vi. Solar furnaces: Large concave mirrors are used to concentrate sunlight to produce heat in a solar furnace.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student used a device (X) to obtain/focus the image of a well illuminated distant building on a screen (S) as shown below in the diagram. Select the correct statement about the device (X).

Explain the following term related to spherical lenses:- optical centre
Define the following term in the context of spherical mirrors:- Principal axis
A concave mirror always forms a real image.
What type of image is formed:
in a plane mirror?
Define (a) centre of curvature (b) radius of curvature (c) pole (d) principal axis, and (e) aperture, of a spherical mirror with the help of a labelled diagram
When a spherical mirror is held towards the sun and its sharp image is formed on a piece of a carbon paper for some time, a hole is burnt in the carbon paper.
What name is given to the distance between spherical mirror and carbon paper?
Name the spherical mirror which can produce a real and diminished image of an object.
A 2.0 cm tall object is placed 40 cm from a diverging lens of focal length 15 cm. Find the position and size of the image.
A coin placed at the bottom of a vessel appears to be raised when water is poured in the vessel.
How is a spherical mirror used to converge a beam of light at a point? Name the type of mirror used.
State the types of mirrors used for (i) headlights and (ii) rear view mirror, in cars and motorcycles. Give to justify your answer in each case.
If a spherical mirror breaks, what type of mirrors are the individual pieces?
What is a spherical mirror?
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a concave mirror for an object placed between its pole and focus. State three characteristics of the image.
Name the mirror which always produces an erect and virtual image. How is the size of image related to the size of object?
What is meant by magnification? Write its expression. What is its sign for the (a) real (b) virtual, image?
How will you distinguish between a plane mirror, a concave mirror and a convex mirror, without touching them?
Upto what maximum distance from a concave mirror, the image can be obtained? What will be the location of object for it?
An object 5 cm high is placed at a distance 60 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. Find the position and size of the image.
An object 5 cm high forms a virtual image of 1.25 cm high, when placed in front of a convex mirror at a distance of 24 cm. Calculate:
- the position of the image
- the focal length of the convex mirror.
Select the correct option:
Which mirror is used in periscope?
Define the following term in relation to concave mirror.
Pole
What do you understand by the term real image?
Does the mirror name by your form a real image for all locations? Give a reason for your answer.
Is real image always inverted?
Complete the following diagrams shown in the below figure by drawing the reflected ray for each incident ray.
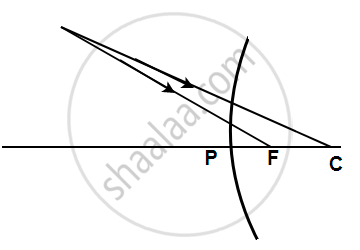
Define the term Pole.
Draw a ray diagram to show that a convex mirror has a wider field of view.
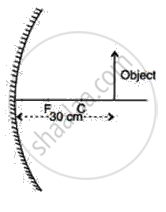
An object is placed in front of a concave mirror as shown in the following figure. By scale drawing, find the nature of the image. Given f = 10 cm, v = 30 cm.
Which of the following has curved reflecting surface?
In torches, search lights and headlights of vehicles the bulb is placed ______.
What is the focal length (f) of a mirror?
What is “aperture”?
A converging lens of focal length f is placed at a distance 0.3 m from an object to produce an image on a screen 0.9 m from the lens. With the object and the screen in the same positions, an image of the object could also be produced on the screen by placing a converging lens of focal length.
Define the following terms in the context of a diverging mirror:
- Principal focus
- Focal length
Draw a labelled ray diagram to illustrate your answer.
