Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Complete the following diagrams shown in the below figure by drawing the reflected ray for each incident ray.
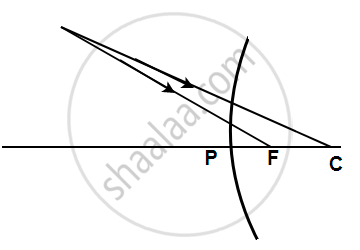
उत्तर
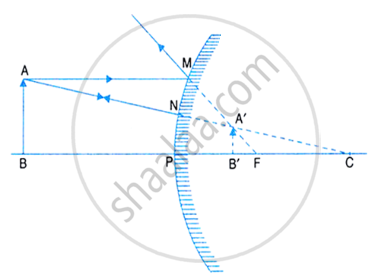
A light ray when produced backwards passes through principal focus as shown in the problem figure. We draw the normal through the centre of curvature at the point of incidence and draw the reflected ray at an angle equal to the angle of incidence thus following the laws of reflection. The reflected ray is parallel to the principal axis. The other ray is passing through the centre of curvature as shown in the problem figure. This ray retraces its incident path because it strikes the mirror normally i.e. 90 degrees. These two reflected rays when produced backwards coincide at a point where the image is formed. The image, A'B' is virtual, erect, and diminished in size.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the following term related to spherical lenses: focal length
An image that cannot be obtained on a screen is called ______.
An image formed by a ______ mirror is always of the same size as that of the object.
When a spherical mirror is held towards the sun and its sharp image is formed on a piece of a carbon paper for some time, a hole is burnt in the carbon paper.
What is the advantage of using a carbon paper rather than a white paper?
The shiny outer surface of a hollow sphere of aluminium of radius 50 cm is to be used as a mirror:
State whether this spherical mirror will diverge or converge light rays.
A lens forms a real image 3 cm high of an object 1 cm high. If the separation of object and image is 15 cm, find the focal length of the lens.
Name the kind of mirror used to obtain
(a) a real and enlarged image
(b) a virtual and enlarged image
(c) a real and diminished image, and
(d) a virtual and diminished image.
An object is placed at 4 cm distance in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 24 cm. Find the position of image. Is the image magnified?
Answer the following question:
Distinguish between the convex mirror and the concave mirror.
